MALDI-TOF MS-Based KPC Direct Detection from Patients' Positive Blood Culture Bottles, Short-Term Cultures, and Colonies at the Hospital
- PMID: 37513712
- PMCID: PMC10385308
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens12070865
MALDI-TOF MS-Based KPC Direct Detection from Patients' Positive Blood Culture Bottles, Short-Term Cultures, and Colonies at the Hospital
Abstract
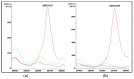
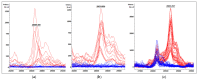
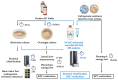
Carbapenemase resistance in Enterobacterales is a global public health problem and rapid and effective methods for detecting these resistance mechanisms are needed urgently. Our aim was to evaluate the performance of a MALDI-TOF MS-based "Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase" (KPC) detection protocol from patients' positive blood cultures, short-term cultures, and colonies in healthcare settings. Bacterial identification and KPC detection were achieved after protein extraction with organic solvents and target spot loading with suitable organic matrices. The confirmation of KPC production was performed using susceptibility tests and blaKPC amplification using PCR and sequencing. The KPC direct detection (KPC peak at approximately 28.681 Da) from patients' positive blood cultures, short-term cultures, and colonies, once bacterial identification was achieved, showed an overall sensibility and specificity of 100% (CI95: [95%, 100%] and CI95: [99%, 100%], respectively). The concordance between hospital routine bacterial identification protocol and identification using this new methodology from the same extract used for KPC detection was ≥92%. This study represents the pioneering effort to directly detect KPC using MALDI-TOF MS technology, conducted on patient-derived samples obtained from hospitals for validation purposes, in a multi-resistance global context that requires concrete actions to preserve the available therapeutic options and reduce the spread of antibiotic resistance markers.
Keywords: KPC; MALDI-TOF MS; blood culture; short-term culture.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MALDI-TOF MS based procedure to detect KPC-2 directly from positive blood culture bottles and colonies.J Microbiol Methods. 2019 Apr;159:120-127. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2019.02.020. Epub 2019 Mar 5. J Microbiol Methods. 2019. PMID: 30849422
-
MALDI-TOF MS-Based Approaches for Direct Identification of Gram-Negative Bacteria and BlaKPC-Carrying Plasmid Detection from Blood Cultures: A Three-Year Single-Centre Study and Proposal of a Diagnostic Algorithm.Microorganisms. 2022 Dec 29;11(1):91. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11010091. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36677383 Free PMC article.
-
A Full MALDI-Based Approach to Detect Plasmid-Encoded KPC-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae.Front Microbiol. 2018 Nov 23;9:2854. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02854. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30542332 Free PMC article.
-
Carbapenemase Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae (KPC): What Is the Best MALDI-TOF MS Detection Method.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Dec 17;10(12):1549. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10121549. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943761 Free PMC article.
-
Direct detection of intact Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemases produced by Enterobacterales using MALDI-TOF MS.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2020 May 1;75(5):1174-1181. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkaa007. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32048718
Cited by
-
Rapid detection of carbapenem-resistant Escherichia coli and carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in positive blood cultures via MALDI-TOF MS and tree-based machine learning models.BMC Microbiol. 2025 Jan 24;25(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12866-025-03755-5. BMC Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39856543 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term culture for rapid identification by mass spectrometry and automated antimicrobial susceptibility testing from positive bottles.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Jun 6;24(1):566. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09475-x. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38844852 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Faccone D., Gomez S.A., de Mendieta J.M., Sanz M.B., Echegorry M., Albornoz E., Lucero C., Ceriana P., Menocal A., Martino F., et al. Emergence of Hyper-Epidemic Clones of Enterobacterales Clinical Isolates Co-Producing KPC and Metallo-Beta-Lactamases during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Pathogens. 2023;12:479. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12030479. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

