The Cellular and Humoral Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 Messenger RNA Vaccines Is Significantly Better in Liver Transplant Patients Compared with Kidney Transplant Patients
- PMID: 37513757
- PMCID: PMC10383075
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens12070910
The Cellular and Humoral Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 Messenger RNA Vaccines Is Significantly Better in Liver Transplant Patients Compared with Kidney Transplant Patients
Abstract
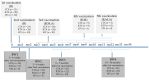
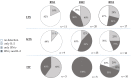
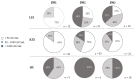
Patients after organ transplantation have impaired immune response after vaccination against the SARS-CoV-2 virus. So far, published studies have reported quite different response rates to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, ranging from 15-79% in liver and kidney transplant recipients. Up to one year after the first vaccine dose, we analyzed the humoral and cellular immune response of 21 liver transplant (LTX) patients after vaccination with mRNA vaccines compared with 28 kidney transplant (KTX) patients. We evaluated IgG against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein as well as SARS-CoV-2 specific T cells using an ELISpot assay that detected IFN-γ- and/or IL-2-expressing T cells. We found a cellular and/or humoral immune response in 100% of the LTX patients compared with 68% of the KTX patients. Antibody titers against the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 were significantly higher in the LTX group, and significantly more LTX patients had detectable specific IL-2-producing T cells. The immunosuppression applied in our LTX cohort was lower compared with the KTX cohort (14% triple therapy in LTX patients vs. 79% in KTX patients). One year after the first vaccination, breakthrough infections could be detected in 41% of all organ transplant patients. None of those patients suffered from a severe course of COVID-19 disease, indicating that a partial vaccination response seemed to offer protection to immunosuppressed patients. The better immune response of LTX patients after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination might be due to less intense immunosuppressive therapy compared with KTX patients.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; immune response; immunosuppression; transplantation; vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Benotmane I., Gautier-Vargas G., Cognard N., Olagne J., Heibel F., Braun-Parvez L., Martzloff J., Perrin P., Moulin B., Fafi-Kremer S., et al. Low immunization rates among kidney transplant recipients who received 2 doses of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Kidney Int. 2021;99:1498–1500. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2021.04.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schramm R., Costard-Jackle A., Rivinius R., Fischer B., Muller B., Boeken U., Haneya A., Provaznik Z., Knabbe C., Gummert J. Poor humoral and T-cell response to two-dose SARS-CoV-2 messenger RNA vaccine BNT162b2 in cardiothoracic transplant recipients. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2021;110:1142–1149. doi: 10.1007/s00392-021-01880-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

