Visual Outcomes of Anti-VEGF Treatment on Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Real-World Population-Based Cohort Study
- PMID: 37513839
- PMCID: PMC10384898
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16070927
Visual Outcomes of Anti-VEGF Treatment on Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Real-World Population-Based Cohort Study
Abstract
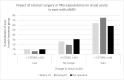
Neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD) leads to visual impairment if not treated promptly. Intravitreal anti-VEGF drugs have revolutionized nAMD treatment in the past two decades. We evaluated the visual outcomes of anti-VEGF treatment in nAMD. A real-life population-based cohort study. The data included parameters for age, sex, age at diagnosis, laterality, chronicity, symptoms, visual outcomes, lens status, and history of intravitreal injections. A total of 1088 eyes (827 patients) with nAMD were included. Visual acuity was stable or improved in 984 eyes (90%) after an average of 36 ± 25 months of follow-up. Bevacizumab was the first-line drug in 1083 (99.5%) eyes. Vision improved ≥15 ETDRS letters in 377 (35%), >5 ETDRS letters in 309 (28%), and was stable (±5 ETDRS letters) in 298 (27%) eyes after anti-VEGF treatment. The loss of 5 ≤ 15 ETDRS letters in 44 (4%) eyes and ≥15 ETDRS letters in 60 (6%) eyes was noted. At the diagnosis of nAMD, 110 out of 827 patients (13%) fulfilled the criteria for visual impairment, whereas 179 patients (22%) were visually impaired after the follow-up. Improvement or stabilization in vision was noted in 90% of the anti-VEGF-treated eyes with nAMD. In addition, anti-VEGF agents are crucial in diminishing nAMD-related visual impairment.
Keywords: anti-VEGF; neovascular age-related macular degeneration; population-based cohort; visual impairment; visual outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wong W.L., Su X., Li X., Cheung C.M.G., Klein R., Cheng C.Y., Wong T.Y. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health. 2014;2:e106–e116. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(13)70145-1. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous