Advances with Lipid-Based Nanosystems for siRNA Delivery to Breast Cancers
- PMID: 37513882
- PMCID: PMC10386415
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16070970
Advances with Lipid-Based Nanosystems for siRNA Delivery to Breast Cancers
Abstract
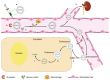
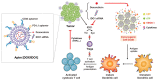
Breast cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer among women. Breast cancer is also the key reason for worldwide cancer-related deaths among women. The application of small interfering RNA (siRNA)-based drugs to combat breast cancer requires effective gene silencing in tumor cells. To overcome the challenges of drug delivery to tumors, various nanosystems for siRNA delivery, including lipid-based nanoparticles that protect siRNA from degradation for delivery to cancer cells have been developed. These nanosystems have shown great potential for efficient and targeted siRNA delivery to breast cancer cells. Lipid-based nanosystems remain promising as siRNA drug delivery carriers for effective and safe cancer therapy including breast cancer. Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) encapsulating siRNA enable efficient and specific silencing of oncogenes in breast tumors. This review discusses a variety of lipid-based nanosystems including cationic lipids, sterols, phospholipids, PEG-lipid conjugates, ionizable liposomes, exosomes for effective siRNA drug delivery to breast tumors, and the clinical translation of lipid-based siRNA nanosystems for solid tumors.
Keywords: breast cancer; gene silencing; lipid NPs; personalized therapy; siRNA delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Breast Cancer Statistics and Resources. [(accessed on 7 June 2023)]. Available online: https://www.bcrf.org/breast-cancer-statistics-and-resources/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

