Cyclic Peptides in Pipeline: What Future for These Great Molecules?
- PMID: 37513908
- PMCID: PMC10386233
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16070996
Cyclic Peptides in Pipeline: What Future for These Great Molecules?
Abstract
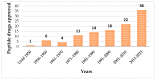
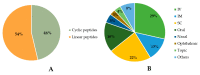
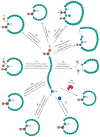
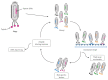
Cyclic peptides are molecules that are already used as drugs in therapies approved for various pharmacological activities, for example, as antibiotics, antifungals, anticancer, and immunosuppressants. Interest in these molecules has been growing due to the improved pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of the cyclic structure over linear peptides and by the evolution of chemical synthesis, computational, and in vitro methods. To date, 53 cyclic peptides have been approved by different regulatory authorities, and many others are in clinical trials for a wide diversity of conditions. In this review, the potential of cyclic peptides is presented, and general aspects of their synthesis and development are discussed. Furthermore, an overview of already approved cyclic peptides is also given, and the cyclic peptides in clinical trials are summarized.
Keywords: bioactivity; clinical trials; cyclic peptides; cyclization; pipeline.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A gold mine for drug discovery: Strategies to develop cyclic peptides into therapies.Med Res Rev. 2020 Mar;40(2):753-810. doi: 10.1002/med.21639. Epub 2019 Oct 9. Med Res Rev. 2020. PMID: 31599007 Review.
-
Elucidating Solution Structures of Cyclic Peptides Using Molecular Dynamics Simulations.Chem Rev. 2021 Feb 24;121(4):2292-2324. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c01087. Epub 2021 Jan 11. Chem Rev. 2021. PMID: 33426882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phage Selection of Cyclic Peptides for Application in Research and Drug Development.Acc Chem Res. 2017 Aug 15;50(8):1866-1874. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00184. Epub 2017 Jul 18. Acc Chem Res. 2017. PMID: 28719188
-
Methods for extraction, isolation and sequencing of cyclotides and others cyclic peptides with anti-helminthic activities: An overview.Parasitol Int. 2024 Feb;98:102808. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2023.102808. Epub 2023 Sep 17. Parasitol Int. 2024. PMID: 37717651 Review.
-
Natural Cyclic Peptides as an Attractive Modality for Therapeutics: A Mini Review.Molecules. 2018 Aug 20;23(8):2080. doi: 10.3390/molecules23082080. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30127265 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Modelling in Bioactive Peptide Discovery and Characterisation.Biomolecules. 2025 Apr 3;15(4):524. doi: 10.3390/biom15040524. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40305228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetically Encoded Levivirus Coat Protein-Based Yeast Display Libraries of Cyclic Peptides.ACS Synth Biol. 2025 Aug 15;14(8):2987-2998. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.4c00873. Epub 2025 Jul 13. ACS Synth Biol. 2025. PMID: 40653716 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Cyclic Peptides: Synthetic Strategies and Biomedical Applications.Biomedicines. 2025 Jan 20;13(1):240. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13010240. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 39857823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and Prospects of Furin Inhibitors for Therapeutic Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 24;25(17):9199. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179199. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors by oligoarginine peptides and polyamine-related compounds.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Dec 15;14:1327603. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1327603. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38169863 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

