Covalent Inhibitors for Neglected Diseases: An Exploration of Novel Therapeutic Options
- PMID: 37513939
- PMCID: PMC10385647
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16071028
Covalent Inhibitors for Neglected Diseases: An Exploration of Novel Therapeutic Options
Abstract
Neglected diseases, primarily found in tropical regions of the world, present a significant challenge for impoverished populations. Currently, there are 20 diseases considered neglected, which greatly impact the health of affected populations and result in difficult-to-control social and economic consequences. Unfortunately, for the majority of these diseases, there are few or no drugs available for patient treatment, and the few drugs that do exist often lack adequate safety and efficacy. As a result, there is a pressing need to discover and design new drugs to address these neglected diseases. This requires the identification of different targets and interactions to be studied. In recent years, there has been a growing focus on studying enzyme covalent inhibitors as a potential treatment for neglected diseases. In this review, we will explore examples of how these inhibitors have been used to target Human African Trypanosomiasis, Chagas disease, and Malaria, highlighting some of the most promising results so far. Ultimately, this review aims to inspire medicinal chemists to pursue the development of new drug candidates for these neglected diseases, and to encourage greater investment in research in this area.
Keywords: Chagas disease; Malaria; covalent target enzyme inhibitors; sleeping sickness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






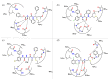

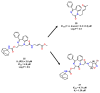
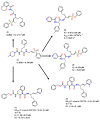
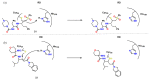










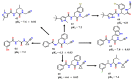

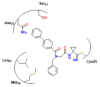
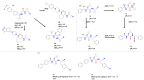
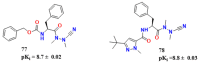











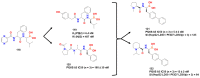
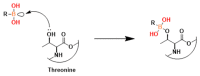
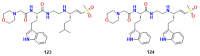


References
-
- Neglected Tropical Diseases. [(accessed on 18 March 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/neglected-tropi....
-
- Cullia G., Bruno S., Parapini S., Margiotta M., Tamborini L., Pinto A., Galbiati A., Mozzarelli A., Persico M., Paladino A., et al. Covalent Inhibitors of Plasmodium falciparum Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase with Antimalarial Activity in Vitro. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019;10:590–595. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.8b00592. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kerr I.D., Wu P., Marion-Tsukamaki R., Mackey Z.B., Brinen L.S. Crystal Structures of TbCatB and Rhodesain, Potential Chemotherapeutic Targets and Major Cysteine Proteases of Trypanosoma brucei. Tschudi, C.; editor. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010;4:e701. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000701. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

