Renoprotective Effect of Chrysanthemum coronarium L. Extract on Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease in Mice
- PMID: 37513959
- PMCID: PMC10383626
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16071048
Renoprotective Effect of Chrysanthemum coronarium L. Extract on Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease in Mice
Abstract
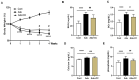
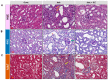
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) gradually leads to loss of renal function and is associated with inflammation and fibrosis. Chrysanthemum coronarium L., a leafy vegetable, possesses various beneficial properties, including anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, and antiproliferative effects. In this study, we investigated the renoprotective effect of Chrysanthemum coronarium L. extract (CC) on adenine (AD)-induced CKD in mice. CKD was induced by feeding mice with an AD diet (0.25% w/w) for 4 weeks. Changes in renal function, histopathology, inflammation, and renal interstitial fibrosis were analyzed. The adenine-fed mice were characterized by increased blood urea nitrogen, serum creatinine, and histological changes, including inflammation and fibrosis; however, these changes were significantly restored by treatment with CC. Additionally, CC inhibited the expression of the inflammatory markers, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, interleukins-6 and -1β, intercellular adhesion molecule-1, and cyclooxygenase 2. Moreover, CC suppressed the expression of the fibrotic markers, type IV collagen, and fibronectin. Furthermore, CC attenuated the expression of profibrotic genes (tumor growth factor-β and α-smooth muscle actin) in AD-induced renal injury mice. Thus, our results suggest that CC has the potential to attenuate AD-induced renal injury and might offer a new option as a renoprotective agent or functional food supplement to manage CKD.
Keywords: Chrysanthemum coronarium L. extract; chronic kidney disease; fibrosis; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Zhang C.-Y., Zhu J.-Y., Ye Y., Zhang M., Zhang L.-J., Wang S.-J., Song Y.-N., Zhang H. Erhuang Formula ameliorates renal damage in adenine–induced chronic renal failure rats via inhibiting inflammatory and fibrotic responses. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017;95:520–528. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.08.115. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sonfack C.S., Nguelefack-Mbuyo E.P., Kojom J.J., Lappa E.L., Peyembouo F.P., Fofié C.K., Nolé T., Nguelefack T.B., Dongmo A.B. The aqueous extract from the stem bark of Garcinia lucida Vesque (Clusiaceae) exhibits cardioprotective and nephroprotective effects in adenine-induced chronic kidney disease in rats. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2021;2021:5581041. doi: 10.1155/2021/5581041. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

