Stable Gastric Pentadecapeptide BPC 157-Possible Novel Therapy of Glaucoma and Other Ocular Conditions
- PMID: 37513963
- PMCID: PMC10385428
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16071052
Stable Gastric Pentadecapeptide BPC 157-Possible Novel Therapy of Glaucoma and Other Ocular Conditions
Abstract
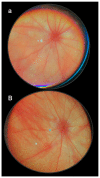
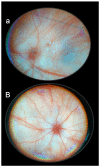
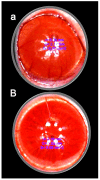
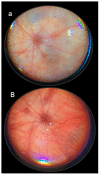
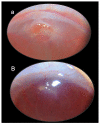
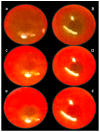
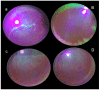
Recently, stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 therapy by activation of collateral pathways counteracted various occlusion/occlusion-like syndromes, vascular, and multiorgan failure, and blood pressure disturbances in rats with permanent major vessel occlusion and similar procedures disabling endothelium function. Thereby, we revealed BPC 157 cytoprotective therapy with strong vascular rescuing capabilities in glaucoma therapy. With these capabilities, BPC 157 therapy can recover glaucomatous rats, normalize intraocular pressure, maintain retinal integrity, recover pupil function, recover retinal ischemia, and corneal injuries (i.e., maintained transparency after complete corneal abrasion, corneal ulceration, and counteracted dry eye after lacrimal gland removal or corneal insensitivity). The most important point is that in glaucomatous rats (three of four episcleral veins cauterized) with high intraocular pressure, all BPC 157 regimens immediately normalized intraocular pressure. BPC 157-treated rats exhibited normal pupil diameter, microscopically well-preserved ganglion cells and optic nerve presentation, normal fundus presentation, nor- mal retinal and choroidal blood vessel presentation, and normal optic nerve presentation. The one episcleral vein rapidly upgraded to accomplish all functions in glaucomatous rats may correspond with occlusion/occlusion-like syndromes of the activated rescuing collateral pathway (azygos vein direct blood flow delivery). Normalized intraocular pressure in glaucomatous rats corresponded to the counteracted intra-cranial (superior sagittal sinus), portal, and caval hypertension, and aortal hypotension in occlusion/occlusion-like syndromes, were all attenuated/eliminated by BPC 157 therapy. Furthermore, given in other eye disturbances (i.e., retinal ischemia), BPC 157 instantly breaks a noxious chain of events, both at an early stage and an already advanced stage. Thus, we further advocate BPC 157 as a therapeutic agent in ocular disease.
Keywords: BPC 157; corneal injuries; glaucomatous rats; intraocular pressure; maintained transparency; pupil function; retinal integrity; retinal ischemia; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
New studies with stable gastric pentadecapeptide protecting gastrointestinal tract. significance of counteraction of vascular and multiorgan failure of occlusion/occlusion-like syndrome in cytoprotection/organoprotection.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Oct;32(5):3119-3161. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01499-8. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38980576 Review.
-
Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 as Therapy for Inferior Caval Vein Embolization: Recovery of Sodium Laurate-Post-Embolization Syndrome in Rats.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Oct 23;16(10):1507. doi: 10.3390/ph16101507. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895979 Free PMC article.
-
Stable Gastric Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 Therapy of Rat Glaucoma.Biomedicines. 2021 Dec 31;10(1):89. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10010089. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 35052769 Free PMC article.
-
Stomach perforation-induced general occlusion/occlusion-like syndrome and stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 therapy effect.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Jul 21;29(27):4289-4316. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i27.4289. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37545637 Free PMC article.
-
Stable Gastric Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 May Recover Brain-Gut Axis and Gut-Brain Axis Function.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Apr 30;16(5):676. doi: 10.3390/ph16050676. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37242459 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Stable Gastric Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 Pleiotropic Beneficial Activity and Its Possible Relations with Neurotransmitter Activity.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Apr 3;17(4):461. doi: 10.3390/ph17040461. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New studies with stable gastric pentadecapeptide protecting gastrointestinal tract. significance of counteraction of vascular and multiorgan failure of occlusion/occlusion-like syndrome in cytoprotection/organoprotection.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Oct;32(5):3119-3161. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01499-8. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38980576 Review.
-
Stable Gastric Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 Therapy: Effect on Reperfusion Following Maintained Intra-Abdominal Hypertension (Grade III and IV) in Rats.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Nov 2;16(11):1554. doi: 10.3390/ph16111554. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004420 Free PMC article.
-
Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 as Therapy for Inferior Caval Vein Embolization: Recovery of Sodium Laurate-Post-Embolization Syndrome in Rats.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Oct 23;16(10):1507. doi: 10.3390/ph16101507. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895979 Free PMC article.
-
Stable Gastric Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 as a Therapy and Safety Key: A Special Beneficial Pleiotropic Effect Controlling and Modulating Angiogenesis and the NO-System.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jun 19;18(6):928. doi: 10.3390/ph18060928. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40573323 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sikiric P., Gojkovic S., Knezevic M., Tepes M., Strbe S., Vukojevic J., Duzel A., Kralj T., Krezic I., Zizek H., et al. Stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157: Prompt particular activation of the collateral pathways. Curr. Med. Chem. 2023;30:1568–1573. doi: 10.2174/0929867329666221005111553. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sikiric P., Udovicic M., Barisic I., Balenovic D., Zivanovic Posilovic G., Strinic D., Uzun S., Sikiric S., Krezic I., Zizek H., et al. Stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 as useful cytoprotective peptide therapy in the hearth disturbances, myocardial infarction, heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, arrhythmias, and thrombosis presentation. Biomedicines. 2022;10:2696. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10112696. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sikiric P., Rucman R., Turkovic B., Sever M., Klicek R., Radic B., Drmic D., Stupnisek M., Misic M., Vuletic L.B., et al. Novel cytoprotective mediator, stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157. Vascular recruitment and gastrointestinal tract healing. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018;24:1990–2001. doi: 10.2174/1381612824666180608101119. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sikiric P., Seiwerth S., Rucman R., Drmic D., Stupnisek M., Kokot A., Sever M., Zoricic I., Zoricic Z., Batelja L., et al. Stress in gastrointestinal tract and stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157. Finally, do we have a solution? Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017;23:4012–4028. doi: 10.2174/1381612823666170220163219. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sikiric P., Seiwerth S., Rucman R., Kolenc D., Vuletic L.B., Drmic D., Grgic T., Strbe S., Zukanovic G., Crvenkovic D., et al. Brain-gut axis and pentadecapeptide BPC 157: Theoretical and practical implications. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016;14:857–865. doi: 10.2174/1570159X13666160502153022. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

