Tablet Geometry Effect on the Drug Release Profile from a Hydrogel-Based Drug Delivery System
- PMID: 37514103
- PMCID: PMC10384981
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071917
Tablet Geometry Effect on the Drug Release Profile from a Hydrogel-Based Drug Delivery System
Abstract
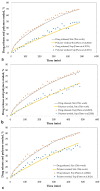
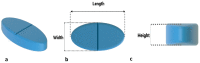
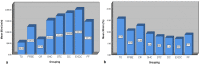
In order to achieve the optimal level of effectiveness and safety of drugs, it is necessary to control the drug release rate. Therefore, it is important to discover the factors affecting release profile from a drug delivery system. Geometry is one of these effective factors for a tablet-shaped drug delivery system. In this study, an attempt has been made to answer a general question of how the geometry of a tablet can affect the drug release profile. For this purpose, the drug release process of theophylline from two hundred HPMC-based tablets, which are categorized into eight groups of common geometries in the production of oral tablets, was simulated using finite element analysis. The analysis of the results of these simulations was carried out using statistical methods including partial least squares regression and ANOVA tests. The results showed that it is possible to predict the drug release profile by knowing the geometry type and dimensions of a tablet without performing numerous dissolution tests. Another result was that, although in many previous studies the difference in the drug release profile from several tablets with different geometries was interpreted only by variables related to the surface, the results showed that regardless of the type of geometry and its dimensions, it is not possible to have an accurate prediction of the drug release profile. Also, the results showed that without any change in the dose of the drug and the ingredients of the tablet and only because of the difference in geometry type, the tablets significantly differ in release profile. This occurred in such a way that, for example, the release time of the entire drug mass from two tablets with the same mass and materials but different geometries can be different by about seven times.
Keywords: AUC; DE; HPMC; MDT; QbD; drug delivery; geometry; hydrogel; mathematical modeling; release profile.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Does the performance of wet granulation and tablet hardness affect the drug dissolution profile of carvedilol in matrix tablets?Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2018 Sep;44(9):1543-1550. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2018.1483394. Epub 2018 Jun 14. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2018. PMID: 29848075
-
The influence of HPMC concentration on release of theophylline or hydrocortisone from extended release mini-tablets.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2013 Aug;39(8):1167-74. doi: 10.3109/03639045.2012.681053. Epub 2012 Apr 27. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2013. PMID: 22540355
-
Influence of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose mixture, apparent viscosity, and tablet hardness on drug release using a 2(3) full factorial design.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2002 May;28(5):601-8. doi: 10.1081/ddc-120003456. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2002. PMID: 12098849
-
New comprehensive mathematical model for HPMC-MCC based matrices to design oral controlled release systems.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2017 Dec;121:61-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2017.09.007. Epub 2017 Sep 22. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2017. PMID: 28951063
-
Mathematical Model-Based Accelerated Development of Extended-release Metformin Hydrochloride Tablet Formulation.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2016 Aug;17(4):1007-13. doi: 10.1208/s12249-015-0423-9. Epub 2015 Oct 19. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2016. PMID: 26729531
Cited by
-
Application of the Quality by Design Concept (QbD) in the Development of Hydrogel-Based Drug Delivery Systems.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Nov 14;15(22):4407. doi: 10.3390/polym15224407. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38006131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What Does Pharmaceutical 3D Printing Cost? A Framework and Case Study with Hydrocortisone for Adrenal Insufficiency.Pharmacoecon Open. 2025 Mar;9(2):207-215. doi: 10.1007/s41669-024-00551-1. Epub 2024 Dec 30. Pharmacoecon Open. 2025. PMID: 39739242 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cam M.E., Yildiz S., Alenezi H., Cesur S., Ozcan G.S., Erdemir G., Edirisinghe U., Akakin D., Kuruca D.S., Kabasakal L. Evaluation of burst release and sustained release of pioglitazone-loaded fibrous mats on diabetic wound healing: An in vitro and in vivo comparison study. J. R. Soc. Interface. 2020;17:20190712. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2019.0712. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gharehnazifam Z., Dolatabadi R., Baniassadi M., Shahsavari H., Kajbafzadeh A.-M., Abrinia K., Gharehnazifam K., Baghani M. Multiphysics modeling and experiments on ultrasound-triggered drug delivery from silk fibroin hydrogel for Wilms tumor. Int. J. Pharm. 2022;621:121787. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121787. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gharehnazifam Z., Dolatabadi R., Baniassadi M., Shahsavari H., Kajbafzadeh A.M., Abrinia K., Baghani M. Computational analysis of vincristine loaded silk fibroin hydrogel for sustained drug delivery applications: Multiphysics modeling and experiments. Int. J. Pharm. 2021;609:121184. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.121184. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

