Research Progress on Stimulus-Responsive Polymer Nanocarriers for Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 37514114
- PMCID: PMC10386740
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071928
Research Progress on Stimulus-Responsive Polymer Nanocarriers for Cancer Treatment
Abstract
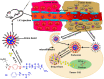
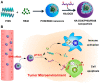
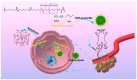
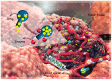
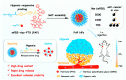
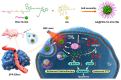
As drug carriers for cancer treatment, stimulus-responsive polymer nanomaterials are a major research focus. These nanocarriers respond to specific stimulus signals (e.g., pH, redox, hypoxia, enzymes, temperature, and light) to precisely control drug release, thereby improving drug uptake rates in cancer cells and reducing drug damage to normal cells. Therefore, we reviewed the research progress in the past 6 years and the mechanisms underpinning single and multiple stimulus-responsive polymer nanocarriers in tumour therapy. The advantages and disadvantages of various stimulus-responsive polymeric nanomaterials are summarised, and the future outlook is provided to provide a scientific and theoretical rationale for further research, development, and utilisation of stimulus-responsive nanocarriers.
Keywords: cancer; carrier; polymer nanomaterials; stimulus-responsive.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Goyal A.K., Rath G., Faujdar C., Malik B. Applications of Targeted Nano Drugs and Delivery Systems. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2019. Application and Perspective of pH-Responsive Nano Drug Delivery Systems; pp. 15–33.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

