Electroacoustic Biosensor Systems for Evaluating Antibiotic Action on Microbial Cells
- PMID: 37514587
- PMCID: PMC10383298
- DOI: 10.3390/s23146292
Electroacoustic Biosensor Systems for Evaluating Antibiotic Action on Microbial Cells
Abstract
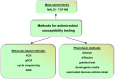
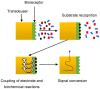
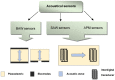
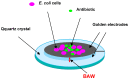
Antibiotics are widely used to treat infectious diseases. This leads to the presence of antibiotics and their metabolic products in the ecosystem, especially in aquatic environments. In many countries, the growth of pathogen resistance to antibiotics is considered a threat to national security. Therefore, methods for determining the sensitivity/resistance of bacteria to antimicrobial drugs are important. This review discusses the mechanisms of the formation of antibacterial resistance and the various methods and sensor systems available for analyzing antibiotic effects on bacteria. Particular attention is paid to acoustic biosensors with active immobilized layers and to sensors that analyze antibiotics directly in liquids. It is shown that sensors of the second type allow analysis to be done within a short period, which is important for timely treatment.
Keywords: acoustic biosensors; acoustic delay lines; antibiotic resistance/sensitivity; bacterial cells; piezoelectric resonators.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Development of Whole-Cell Biosensors for Screening of Peptidoglycan-Targeting Antibiotics in a Gram-Negative Bacterium.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Sep 22;88(18):e0084622. doi: 10.1128/aem.00846-22. Epub 2022 Aug 30. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36040151 Free PMC article.
-
Optical and Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors for the Detection of Quinolones.Trends Biotechnol. 2019 Aug;37(8):898-915. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2019.01.004. Epub 2019 Feb 15. Trends Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30777309 Review.
-
Biosensor applications in the field of antibiotic research--a review of recent developments.Sensors (Basel). 2011;11(10):9450-66. doi: 10.3390/s111009450. Epub 2011 Oct 3. Sensors (Basel). 2011. PMID: 22163705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Innovations in Bacterial Infection Detection and Treatment.ACS Infect Dis. 2021 Apr 9;7(4):695-720. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00890. Epub 2021 Mar 18. ACS Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33733747 Review.
-
New approach for determination of antimicrobial susceptibility to antibiotics by an acoustic sensor.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Feb;104(3):1283-1290. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-10295-2. Epub 2019 Dec 21. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31865437
Cited by
-
The expression of different gene constructs in Escherichia coli SM lux biosensor after exposure to drugs.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 30;14(1):31899. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-83190-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39738597 Free PMC article.
-
Piezoelectric Chemosensors and Biosensors in Medical Diagnostics.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Mar 20;15(3):197. doi: 10.3390/bios15030197. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40136994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights into the roles of fungi and bacteria in the development of medicinal plant.J Adv Res. 2024 Nov;65:137-152. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.12.007. Epub 2023 Dec 12. J Adv Res. 2024. PMID: 38092299 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Martín D.S., Wrande M., Sandegren L., Zardán Gómez de la Torre T. Naked-eye detection of antibiotic resistance gene sul1 based on aggregation of magnetic nanoparticles and DNA amplification products. Biosens. Bioelectron. X. 2022;12:100277. doi: 10.1016/j.biosx.2022.100277. - DOI
-
- Liu C., Li B., Liu M., Mao S. Demand, status, and prospect of antibiotics detection in the environment. Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem. 2022;369:132383. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2022.132383. - DOI
-
- Cháfer-Pericás C., Maquieira Á., Puchades R. Fast screening methods to detect antibiotic residues in food samples. Trends Anal. Chem. 2010;29:1038–1049. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2010.06.004. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

