The Prospective COVID-19 Post-Immunization Serological Cohort in Munich (KoCo-Impf): Risk Factors and Determinants of Immune Response in Healthcare Workers
- PMID: 37515259
- PMCID: PMC10383736
- DOI: 10.3390/v15071574
The Prospective COVID-19 Post-Immunization Serological Cohort in Munich (KoCo-Impf): Risk Factors and Determinants of Immune Response in Healthcare Workers
Abstract
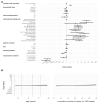
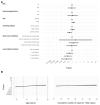
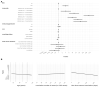
Antibody studies analyze immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination and infection, which is crucial for selecting vaccination strategies. In the KoCo-Impf study, conducted between 16 June and 16 December 2021, 6088 participants aged 18 and above from Munich were recruited to monitor antibodies, particularly in healthcare workers (HCWs) at higher risk of infection. Roche Elecsys® Anti-SARS-CoV-2 assays on dried blood spots were used to detect prior infections (anti-Nucleocapsid antibodies) and to indicate combinations of vaccinations/infections (anti-Spike antibodies). The anti-Spike seroprevalence was 94.7%, whereas, for anti-Nucleocapsid, it was only 6.9%. HCW status and contact with SARS-CoV-2-positive individuals were identified as infection risk factors, while vaccination and current smoking were associated with reduced risk. Older age correlated with higher anti-Nucleocapsid antibody levels, while vaccination and current smoking decreased the response. Vaccination alone or combined with infection led to higher anti-Spike antibody levels. Increasing time since the second vaccination, advancing age, and current smoking reduced the anti-Spike response. The cumulative number of cases in Munich affected the anti-Spike response over time but had no impact on anti-Nucleocapsid antibody development/seropositivity. Due to the significantly higher infection risk faced by HCWs and the limited number of significant risk factors, it is suggested that all HCWs require protection regardless of individual traits.
Keywords: COVID-19; ORCHESTRA; SARS-CoV-2; antibodies; breakthrough infections; health care workers; immunologic response; seroprevalence; vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
In addition to the funding disclosed in the funding section, AW and MH report personal fees and non-financial support from Roche Diagnostics, non-financial support from Euroimmun, non-financial support from Viramed, and non-financial support from Mikrogen. AW and MH report grants, non-financial support and other from German Centre for Infection Research DZIF, grants and non-financial support from Government of Bavaria, non-financial support from BMW, non-financial support from Munich Police, non-financial support and other from Accenture. MH and AW report personal fees and non-financial support received from Box-Betrobox and non-financial support from Becker MVZ during the conduction of this study. AW is involved in other different patents and companies, not in relation to the serology of SARS-CoV-2. AW reports personal fees and others from Haeraeus Sensors and non-financial support from Bruker Daltonics, all of which are outside the submitted work and non-related to SARS-CoV-2. The funders had no role in this study’s design, data collection, data analyses, data interpretation, writing, or submission of this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19—11 March 2020. [(accessed on 13 April 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-genera....
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 13 April 2023)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- RKI Table Showing Current COVID-19 Infections per Day as Time Series. [(accessed on 16 October 2022)]. Available online: https://npgeo-corona-npge-de.hub.arcgis.com/datasets/dd4580c810204019a7b....
-
- RKI Tabelle mit den Gemeldeten Impfungen nach Bundesländern und Impfquoten nach Altersgruppen. [(accessed on 16 September 2021)]. Available online: https://www.rki.de/DE/Content/InfAZ/N/Neuartiges_Coronavirus/Daten/Impfq....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

