E-cigarettes and arrhythmogenesis: a comprehensive review of pre-clinical studies and their clinical implications
- PMID: 37517059
- PMCID: PMC10578912
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvad113
E-cigarettes and arrhythmogenesis: a comprehensive review of pre-clinical studies and their clinical implications
Abstract
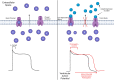
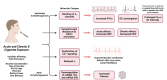
Electronic cigarette use has grown exponentially in recent years, and while their popularity has increased, the long-term effects on the heart are yet to be fully studied and understood. Originally designed as devices to assist with those trying to quit traditional combustible cigarette use, their popularity has attracted use by teens and adolescents who traditionally have not smoked combustible cigarettes. Acute effects on the heart have been shown to be similar to traditional combustible cigarettes, including increased heart rate and blood pressure. The main components of electronic cigarettes that contribute to these arrhythmic effects are found in the e-liquid that is aerosolized and inhaled, comprised of nicotine, flavourings, and a combination of vegetable glycerin (VG) and propylene glycol (PG). Nicotine can potentially induce both ventricular and atrial arrhythmogenesis, with both the atrial and ventricular effects resulting from the interactions of nicotine and the catecholamines they release via potassium channels. Atrial arrhythmogenesis, more specifically atrial fibrillation, can also occur due to structural alterations, which happens because of nicotine downregulating microRNAs 133 and 590, both post-transcriptional growth factor repressors. Liquid flavourings and the combination of PG and VG can possibly lead to arrhythmic events by exposing users to acrolein, an aldehyde that stimulates TRPA1 that in turn causes a change towards sympathetic activation and autonomic imbalance. The design of these electronic delivery devices is constantly changing; therefore, it has proven extremely difficult to study the long-term effects on the heart caused by electronic cigarettes but will be important to understand given their rising popularity. The arrhythmic effects of electronic cigarettes appear similar to traditional cigarettes as well; however, a comprehensive review has not been compiled and is the focus of this article.
Keywords: Arrhythmia; Cardiac effects; Electronic cigarette; Electronic nicotine delivery systems.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Dinardo P, Rome ES. Vaping: the new wave of nicotine addiction. Cleve Clin J Med 2019;86:789–798. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

