Exploring genetic risk for catatonia in a genome wide association study and polygenic risk score analysis
- PMID: 37517919
- PMCID: PMC10822029
- DOI: 10.1016/j.schres.2023.07.015
Exploring genetic risk for catatonia in a genome wide association study and polygenic risk score analysis
Abstract
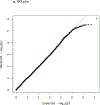
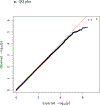
Background: Catatonia is an under-recognized disorder characterized by psychomotor (increased, decreased, or abnormal) changes, affective symptoms, and disturbance of volition, which may arise in the setting of decompensated psychiatric or non-psychiatric medical disorders. Genetic studies of catatonia are limited, and to the best of our knowledge no prior genome wide association studies of catatonia have been performed to date.
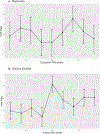
Methods: First we performed a genome wide association study of catatonia regardless of etiology (psychiatric or non-psychiatric). Secondarily we evaluated whether there was an elevated genetic risk profile for predisposing psychiatric disorders (schizophrenia spectrum disorder, bipolar affective disorder, etc.) in patients with catatonia. We used a matched case control design and applied polygenic risk scores to evaluate for a shared polygenetic contribution to catatonia from common psychiatric phenotypes that show a high prevalence of catatonia in their decompensated states.
Results: Anxiety, bipolar affective disorder, schizophrenia spectrum disorder and cross disorder polygenic risk scores were significantly associated with catatonia case status in both unadjusted and adjusted logistic regression models for the European Ancestry set even after correcting for multiple comparisons. Depression, Alzheimer's, Autism Spectrum Disorder and Obsessive Disorder polygenic risk scores were not significantly associated with catatonia status in participants of European Ancestry. In the African Ancestry set, no psychiatric polygenic risk scores were significantly associated with catatonia status in either the unadjusted or adjusted regression models.
Conclusions: Even after controlling for relevant covariates, anxiety, bipolar affective disorder, schizophrenia spectrum disorder and cross disorders were significantly associated with catatonia status suggesting that there might be a shared genetic risk for those disorders amongst patients with catatonia.
Keywords: Catatonia; Genetics; Polygenic risk; Schizophrenia.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors disclose that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be seen as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Abrams R, Taylor MA, 1976. Catatonia. A prospective clinical study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 33(5), 579–581. - PubMed
-
- Abrams R, Taylor MA, 1977. Catatonia: prediction of response to somatic treatments. Am J Psychiatry 134(1), 78–80. - PubMed
-
- Abrams R, Taylor MA, Coleman Stolurow KA, 1979. Catatonia and mania: patterns of cerebral dysfunction. Biol Psychiatry 14(1), 111–117. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association, 2013. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000445/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 HL065962/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR025141/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY008126/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD074711/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 GM092618/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM115305/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS032830/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD103537/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006378/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004798/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002243/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

