Role of acoustic radiation force impulse elastography of placenta in the diagnosis of pre-eclampsia
- PMID: 37518824
- PMCID: PMC11333396
- DOI: 10.1007/s40477-023-00801-8
Role of acoustic radiation force impulse elastography of placenta in the diagnosis of pre-eclampsia
Abstract
Background: Placental dysfunction is one of the main causes of preeclampsia and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy.
Material and methods: This is a prospective comparative study done on 30 pregnant women with pre-eclampsia and another 30 pregnant women as controls. In all these subjects the elasticity of the placenta was measured.
Results: The results obtained showed that there was a significant difference in SWV values between the two groups (p value = 0.001). The mean SWV value of normal pregnant women was 0.99 m/ second as opposed to 1.99 m/second in pre-eclamptic pregnant women.
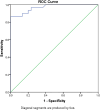
Conclusion: Sonoelastography is a promising noninvasive tool in the detection of preeclampsia with high diagnostic accuracy. The SWV values measured at the central zones of the placenta with a cut-off value of 1.325 m/s identify the presence of pre-eclampsia with high sensitivity and specificity.
Keywords: Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography (ARFI); Pre-eclampsia; Shear wave velocity.
© 2023. Società Italiana di Ultrasonologia in Medicina e Biologia (SIUMB).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures









References
-
- Arizawa M, Nakayama M (1992) Pathological analysis of the placenta in trisomies 21, 18 and 13. Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi. 144(1):9–13 - PubMed
-
- Karaman E, Arslan H, Çetin O, Şahin HG, Bora A, Yavuz A, Elasan S, Akbudak İ (2016) Comparison of placental elasticity in normal and pre-eclamptic pregnant women by acoustic radiation force impulse elastosonography. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 42(11):1464–1470. 10.1111/jog.13078 10.1111/jog.13078 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Huwart L, Sempoux C, Vicaut E, Salameh N, Annet L, Danse E, Peeters F, ter Beek LC, Rahier J, Sinkus R, Horsmans Y, Van Beers BE (2008) Magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive staging of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 135(1):32–40. 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.076 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.076 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

