Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on paediatric otolaryngology: a nationwide study
- PMID: 37519138
- PMCID: PMC10551727
- DOI: 10.14639/0392-100X-N2452
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on paediatric otolaryngology: a nationwide study
Abstract
Objective: The COVID-19 pandemic profoundly modified the work routine in healthcare; however, its impact on the field of paediatric otorhinolaryngology (ORL) has been rarely investigated. The aim of this study was to assess the impact of COVID-19 on paediatric ORL.
Methods: A questionnaire was developed by the Young Otolaryngologists of the Italian Society of ORL-Head and Neck Surgery (GOS). The questionnaire consisted of 26 questions related to workplace and personal paediatric ORL activities. The link was advertised on the official social media platforms and sent by e-mail to 469 Italian otolaryngologists.
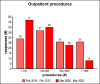
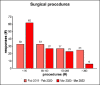
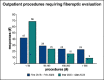
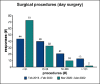
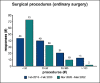
Results: The questionnaire was completed by 118 responders. During the pandemic, the main reduction was observed for surgical activity (78.8%), followed by outpatient service (16.9%). The conditions that were mostly impacted by a delayed diagnosis were respiratory infections in 45.8% of cases and sensorineural hearing loss in 37.3% of cases.
Conclusions: Paediatric ORL was highly impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic, with a significant reduction of surgical and outpatient activities and a delay in time-sensitive diagnosis. Therefore, the implementation of new strategies, such as telemedicine, is recommended.
Impatto della pandemia COVID-19 sull’otorinolaringoiatria pediatrica.
Obiettivo: L’impatto della pandemia COVID-19 sul settore dell’otorinolaringoiatria (ORL) pediatrica è stato poco studiato. Lo scopo di questa ricerca è stato, pertanto, quello di valutare l’impatto del COVID-19 sull’ORL pediatrica, concentrandosi sulle differenze con il periodo precedente la pandemia.
Metodi: Un questionario composto da 26 domande relative alle attività lavorative è stato sviluppato dal Gruppo Giovani della Società Italiana di ORL e Chirurgia Cervico-facciale (GOS). Il link è stato diffuso sui social media della società e inviato via e-mail a 469 otorinolaringoiatri.
Risultati: Il questionario è stato compilato da 118 otorinolaringoiatri. Durante la pandemia, la principale riduzione è stata osservata per l’attività chirurgica (78,8%), seguita dal servizio ambulatoriale (16,9%). Le condizioni maggiormente colpite da una diagnosi ritardata sono state le infezioni respiratorie nel 45,8% e l’ipoacusia neurosensoriale nel 37,3%.
Conclusioni: L’ORL pediatrica è stata influenzata dalla pandemia COVID-19 con una riduzione statisticamente significativa delle attività chirurgiche e ambulatoriali. Molte diagnosi che necessitano di un trattamento tempestivo sono state differite. Pertanto, si raccomanda di implementare nuove strategie, come la telemedicina.
Keywords: COVID-19; adenoidectomy; children; paediatric otolaryngology; tonsillectomy.
Copyright © 2023 Società Italiana di Otorinolaringoiatria e Chirurgia Cervico-Facciale, Rome, Italy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ralli M, Mannelli G, Bonali M, et al. Impact of COVID-19 on otolaryngology in Italy: a commentary from the COVID-19 task force of the Young Otolaryngologists of the Italian Society of Otolaryngology. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2020;24:7516-7518. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202007_21925 10.26355/eurrev_202007_21925 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mannelli G, Ralli M, Bonali M, et al. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on Italian Otolaryngology Units: a nationwide study. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 2020;40:325-331. https://doi.org/10.14639/0392-100X-N0832 10.14639/0392-100X-N0832 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gelardi M, Iannuzzi L, Trecca EMC, et al. COVID-19: what happened to all of the otolaryngology emergencies? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2020;277:3231-3232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-06046-z 10.1007/s00405-020-06046-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mahendran GN, Tey CS, Musso MF, et al. Measuring the impact of a delay in care on pediatric otolaryngologic surgery completion. Ear Nose Throat J 2022. Oct 14:1455613221134428. https://doi.org/10.1177/01455613221134428 10.1177/01455613221134428 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gelardi M, Giancaspro R, Fiore V, et al. COVID-19: effects of lockdown on adenotonsillar hypertrophy and related diseases in children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2020;138:110284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2020.110284 10.1016/j.ijporl.2020.110284 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

