Ultra-weak photon emission as a potential tool for evaluating the therapeutic effect of traditional Chinese medicine in patients with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 37519692
- PMCID: PMC10372244
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18055
Ultra-weak photon emission as a potential tool for evaluating the therapeutic effect of traditional Chinese medicine in patients with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Background: Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has been used to prevent and treat type 2 diabetes (T2DM) for thousands of years. The holistic view of TCM and the "multitarget" characteristics of Chinese medicine have unique advantages in the prevention and treatment of T2DM. TCM syndrome differentiation and treatment are effective for T2DM; however, currently, the therapeutic effect of TCM is generally evaluated by asking for patients' subjective feelings, or by checking the changes in relevant indicators. The main problems are that the patient's descriptions are unclear and subjective, and although the self-reported symptoms may have improved significantly, the relevant indicators are sometimes not obvious, which cannot truly reflect the therapeutic effect of TCM. Therefore, it is urgent to develop a novel, sensitive, and noninvasive method to quantitatively evaluate the therapeutic effect of TCM.
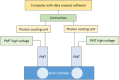
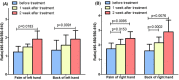
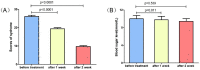
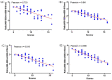
Methods: In this study, ultra-weak photon emission (UPE) was measured at four sites of hands of T2DM patients with Qi-Yin deficiency before treatment and after 1 and 2 weeks of treatment with TCM. The UPE intensity and spectral distribution were calculated and analyzed using the results measured at these four sites. Spearman's correlation coefficient was used to quantify the correlation between the UPE parameters and the syndrome scores of TCM.
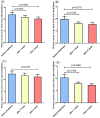
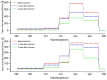
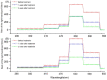
Results: The UPE intensity of T2DM patients with Qi-Yin deficiency decreased gradually with the course of the treatment and was significantly lower than that before the treatment. The ratio of photon counts between the wavelength ranges of 495-550 nm and 550-610 nm after the treatment was higher than that before the treatment and negatively correlated with the corresponding syndrome scores so that the degree of symptoms improvement could be characterized by the ratio (495-550 nm/550-610 nm).
Conclusions: The therapeutic effect of TCM in T2DM patients with Qi-Yin deficiency can be shown at the level of UPE. UPE is a potential and noninvasive tool for evaluating the therapeutic effect of TCM in patients with T2DM.
Keywords: Noninvasive; Syndrome of TCM; Therapeutic effect; Type 2 diabetes; Ultra-weak photon emission (UPE).
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- International Diabetes Federation . tenth ed. International Diabetes Federation; Brussels,Belgium: 2021. IDF Diabetes Atlas.
-
- Tian J.X., Zhao L.H., Lian F.M., Tong X.L. Review on the research progress of traditional Chinese medicine in the prevention and treatment of diabetes. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2015;56(24):2093–2097. doi: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r. 2015.24.006. - DOI
-
- Zhu C.L. Evaluation of curative effect of traditional Chinese medicine combined with insulin pump in the treatment of newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes patients with Qi Yin deficiency syndrome. Henan Med. Res. 2021;30(18):3405–3407. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-437X.2021.18.045. - DOI
-
- Xia C.D. Reflection on the evaluation method of clinical efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 2022;8:1–5. 10. 7661/j. cjim. 20220415. 071.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

