Investigating the validity and reliability of the GLFS-25 questionnaire by factor analysis in the elderly hospitalized at the intensive and cardiac care units
- PMID: 37519703
- PMCID: PMC10372237
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18111
Investigating the validity and reliability of the GLFS-25 questionnaire by factor analysis in the elderly hospitalized at the intensive and cardiac care units
Abstract
Introduction: Geriatric Locomotive Function Scale-25 (GLFS-25) is a 25-item tool most commonly used to diagnose locomotive syndrome in the elderly. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the validity and reliability of the GLFS-25 questionnaire using factor analysis.
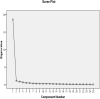
Materials and methods: This descriptive-analytical study was conducted on 186 elderly people. The GLFS-25 questionnaire contains 25 items, and each item is scored on a five-point Likert scale from 0 to 4. Data were analyzed by SPSS V.19 software. Descriptive (frequency, percentage, mean, and standard deviation) and inferential (Cronbach's alpha, correlation coefficient, Bartlett test, KMO index, scree plot, and factor analysis) statistics were used to present the findings.
Results: Factor analysis revealed two hidden factors in the four dimensions of the questionnaire (i.e., pain, daily activities, social relations, and mental health). The first factor, named mobility and its consequential concerns), with a variance percentage of 74.323, had an effect on questions No. 19, 11, 25, 16, 6, 24, 5, 4, and 3. The second factor, named the problems and risks associated with daily and social activities, with a variance percentage of 78.680, had an effect on questions No. 17, 22, 7, 18, 14, 20, 13, 9, 12, 8, 10, 21, 2, 15, 1, and 23. Cronbach's alpha coefficient among the questionnaire's dimensions was 78.4%.
Conclusion: The GLFS-25 questionnaire can be used as a valid and reliable tool to diagnose locomotive syndrome in the elderly.
Keywords: Elderly; Factor analysis; Locomotive syndrome.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reliability and validity tests of the Chinese version of the Geriatric Locomotive Function Scale (GLFS-25) in tumor survivors.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 17;10(9):e29604. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29604. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38694053 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a screening tool for risk of locomotive syndrome in the elderly: the 25-question Geriatric Locomotive Function Scale.J Orthop Sci. 2012 Mar;17(2):163-72. doi: 10.1007/s00776-011-0193-5. Epub 2012 Jan 6. J Orthop Sci. 2012. PMID: 22222445
-
Assessment of locomotive syndrome among older individuals: a confirmatory factor analysis of the 25-question Geriatric Locomotive Function Scale.PeerJ. 2020 Apr 14;8:e9026. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9026. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32328357 Free PMC article.
-
Locomotive Syndrome and Lumbar Spine Disease: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2022 Feb 27;11(5):1304. doi: 10.3390/jcm11051304. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35268395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Locomotive Syndrome: Operational Definition Based on a Questionnaire, and Exercise Interventions on Mobility Dysfunction in Elderly People.Clin Rev Bone Miner Metab. 2016;14:119-130. doi: 10.1007/s12018-016-9210-8. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Clin Rev Bone Miner Metab. 2016. PMID: 27375372 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Rasch Analysis of the 25-Item Geriatric Locomotive Function Scale (GLFS-25) in Japanese Older Adults With Musculoskeletal Disorders: Identifying Age-Related Differences in Terms of Item Difficulty and Misfitting Items.Cureus. 2025 Jun 10;17(6):e85735. doi: 10.7759/cureus.85735. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40656381 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability and validity tests of the Chinese version of the Geriatric Locomotive Function Scale (GLFS-25) in tumor survivors.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 17;10(9):e29604. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29604. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38694053 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akahane M., et al. The impact of musculoskeletal diseases on the presence of locomotive syndrome, Modern. Rheumatology. 2018;29(1):151–156. 2018. - PubMed
-
- Saleh M., et al. Old-Old elderly problems which can be effective in choosing their own bed. J. Geriat. Nurs. 2018;4(2):20–34.
-
- Sadeghimahalli N., et al. Locomotive syndrome in the elderly and its risk factors, Salmand. Iran. J. Age. 2019;13:604–613.
-
- Kobayashi T., et al. The association of comorbidities with the 25-question geriatric locomotive function scale and the diagnosis of locomotive syndrome. J. Orthop. Sci. 2023;28(2):453–459. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources