Assessment of intrafraction motion and its dosimetric impact on prostate radiotherapy using an in-house developed position monitoring system
- PMID: 37519787
- PMCID: PMC10375704
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1082391
Assessment of intrafraction motion and its dosimetric impact on prostate radiotherapy using an in-house developed position monitoring system
Abstract
Purpose: To implement an in-house developed position monitoring software, SeedTracker, for conventional fractionation prostate radiotherapy, and study the effect on dosimetric impact and intrafraction motion.
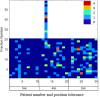
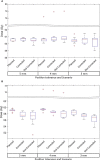
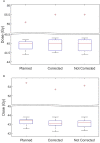
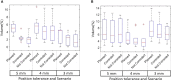
Methods: Thirty definitive prostate radiotherapy patients with implanted fiducial markers were included in the study. All patients were treated with VMAT technique and plans were generated using the Pinnacle planning system using the 6MV beam model for Elekta linear accelerator. The target dose of 60 Gy in 20 fractions was prescribed for 29 of 30 patients, and one patient was treated with the target dose of 78 Gy in 39 fractions. The SeedTracker position monitoring system, which uses the x-ray images acquired during treatment delivery in the Elekta linear accelerator and associated XVI system, was used for online prostate position monitoring. The position tolerance for online verification was progressively reduced from 5 mm, 4 mm, and to 3 mm in 10 patient cohorts to effectively manage the treatment interruptions resulting from intrafraction motion in routine clinical practice. The delivered dose to target volumes and organs at risk in each of the treatment fractions was assessed by incorporating the observed target positions into the original treatment plan.
Results: In 27 of 30 patients, at least one gating event was observed, with a total of 177 occurrences of position deviation detected in 146 of 619 treatment fractions. In 5 mm, 4 mm, and 3 mm position tolerance cohorts, the position deviations were observed in 13%, 24%, and 33% of treatment fractions, respectively. Overall, the mean (range) deviation of -0.4 (-7.2 to 5.3) mm, -0.9 (-6.1 to 15.6) mm, and -1.7 (-7.0 to 6.1) mm was observed in Left-Right, Anterior-Posterior, and Superior-Inferior directions, respectively. The prostate CTV D99 would have been reduced by a maximum value of 1.3 Gy compared to the planned dose if position deviations were uncorrected, but with corrections, it was 0.3 Gy. Similarly, PTV D98 would have been reduced by a maximum value of 7.6 Gy uncorrected, with this difference reduced to 2.2 Gy with correction. The V60 to the rectum increased by a maximum of 1.0% uncorrected, which was reduced to 0.5%.
Conclusion: Online target position monitoring for conventional fractionation prostate radiotherapy was successfully implemented on a standard Linear accelerator using an in-house developed position monitoring software, with an improvement in resultant dose to prostate target volume.
Keywords: delivered dose assessment; intrafraction motion; online position monitoring; prostate radiotherapy; standard linear accelerator; treatment accuracy.
Copyright © 2023 Arumugam, Young, Do, Chlap, Tawfik, Udovitch, Wong and Sidhom.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Palma D, Vollans E, James K, Nakano S, Moiseenko V, Shaffer R, et al. Volumetric modulated arc therapy for delivery of prostate radiotherapy: comparison with intensity-modulated radiotherapy and three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys (2008) 72(4):996–1001. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.02.047 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

