Prognostic scoring system based on eosinophil- and basophil-related markers for predicting the prognosis of patients with stage II and stage III colorectal cancer: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 37519795
- PMCID: PMC10375403
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1182944
Prognostic scoring system based on eosinophil- and basophil-related markers for predicting the prognosis of patients with stage II and stage III colorectal cancer: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Systemic inflammation is associated with the prognosis of colorectal cancer (CRC). The current study aimed to construct a comprehensively inflammatory prognostic scoring system named risk score (RS) based on eosinophil- and basophil-related markers and assess its prognostic value in patients with stage II and stage III CRC.
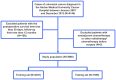
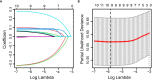
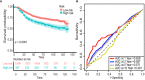
Patients and methods: A total of 3,986 patients were enrolled from January 2007 to December 2013. The last follow-up time was January 2019. They were randomly assigned to the training set and testing set in a 3:2 split ratio. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO)-Cox regression analysis was performed to select the optimal prognostic factors in the construction of RS. The Kaplan-Meier curve, time-dependent receiver operating characteristic (ROC), and Cox analysis were used to evaluate the association between RS and overall survival (OS).
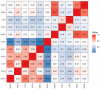
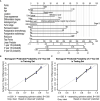
Results: In the training set, all inflammatory markers showed certain prognostic values. Based on LASSO-Cox analysis, nine markers were integrated to construct RS. The Kaplan-Meier curve showed that a higher RS (RS > 0) had a significantly worse prognosis (log-rank p< 0.0001). RS (>0) remained an independent prognostic factor for OS (hazard ratio (HR): 1.70, 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.43-2.03, p< 0.001). The prognostic value of RS was validated in the entire cohort. Time-dependent ROC analysis showed that RS had a stable prognostic effect throughout the follow-up times and could enhance the prognostic ability of the stage by combination. Nomogram was established based on RS and clinicopathological factors for predicting OS in the training set and validated in the testing set. The area under the curve (AUC) values of the 3-year OS in the training and testing sets were 0.748 and 0.720, respectively. The nomogram had a satisfactory predictive accuracy and had better clinical application value than the tumor stage alone.
Conclusions: RS might be an independent prognostic factor for OS in patients with stage II and III CRC, which is helpful for risk stratification of patients. Additionally, the nomogram might be used for personalized prediction and might contribute to formulating a better clinical treatment plan.
Keywords: basophils; biomarker; colorectal cancer; eosinophils; inflammation; prognosis; risk score.
Copyright © 2023 Gao, Yuan, Fu, Tian, Huang, Zhang, Li, Liu, Meng, Liu, Zhang, Xu, Jia, Zhang, Zheng, Fu, Tan, Lan, Yang, Zhao and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

