Measurement of brainstem diameter in small-breed dogs using magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 37519998
- PMCID: PMC10374218
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1183412
Measurement of brainstem diameter in small-breed dogs using magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
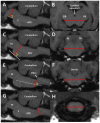
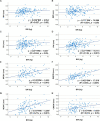
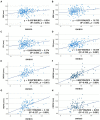
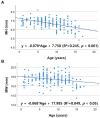
Measurement of brainstem diameters (midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata)is of potential clinical significance, as changes in brainstem size may decrease or increase due to age, neurodegenerative disorders, or neoplasms. In human medicine, numerous studies have reported the normal reference range of brainstem size, which is hitherto unexplored in veterinary medicine, particularly for small-breed dogs. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the reference range of brainstem diameters in small-breed dogs and to correlate the measurements with age, body weight (BW), and body condition score (BCS). Herein, magnetic resonance (MR) images of 544 small-breed dogs were evaluated. Based on the exclusion criteria, 193 dogs were included in the midbrain and pons evaluation, and of these, 119 dogs were included in the medulla oblongata evaluation. Using MR images, the height and width of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata were measured on the median and transverse plane on the T1-weighted image. For the medulla oblongata, two points were measured for each height and width. The mean values of midbrain height (MH), midbrain width (MW), pons height (PH), pons width (PW), medulla oblongata height at the fourth ventricle level (MOHV), medulla oblongata height at the cervicomedullary (CM) junction level (MOHC), rostral medulla oblongata width (RMOW), and caudal medulla oblongata width (CMOW) were 7.18 ± 0.56 mm, 17.42 ± 1.21 mm, 9.73 ± 0.64 mm, 17.23 ± 1.21 mm, 6.06 ± 0.53 mm, 5.77 ± 0.40 mm, 18.93 ± 1.25 mm, and 10.12 ± 1.08 mm, respectively. No significant differences were found between male and female dogs for all the measurements. A negative correlation was found between age and midbrain diameter, including MH (p < 0.001) and MW (p = 0.002). All brainstem diameters were correlated positively with BW (p < 0.05). No significant correlation was found between BCS and all brainstem diameters. Brainstem diameters differed significantly between breeds (p < 0.05), except for MW (p = 0.137). This study assessed linear measurements of the brainstem diameter in small-breed dogs. We suggest that these results could be useful in assessing abnormal conditions of the brainstem in small-breed dogs.
Keywords: age; body weight; brainstem; canine; medulla oblongata; midbrain; pons; size.
Copyright © 2023 Kim, Kwon, Kim, Lee and Yoon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A small pons as a characteristic finding in Down syndrome: A quantitative MRI study.Brain Dev. 2017 Apr;39(4):298-305. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2016.10.016. Epub 2016 Nov 16. Brain Dev. 2017. PMID: 27865668
-
Medulla oblongata volume as a promising predictor of survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Neuroimage Clin. 2022;34:103015. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2022.103015. Epub 2022 Apr 22. Neuroimage Clin. 2022. PMID: 35561555 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroanatomical MRI study: reference values for the measurements of brainstem, cerebellar vermis, and peduncles.Br J Radiol. 2021 Apr 1;94(1120):20201353. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20201353. Epub 2021 Feb 17. Br J Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33571018 Free PMC article.
-
Midbrain, Pons, and Medulla: Anatomy and Syndromes.Radiographics. 2019 Jul-Aug;39(4):1110-1125. doi: 10.1148/rg.2019180126. Radiographics. 2019. PMID: 31283463 Review.
-
Paediatric brainstem: A comprehensive review of pathologies on MR imaging.Insights Imaging. 2016 Aug;7(4):505-22. doi: 10.1007/s13244-016-0496-3. Epub 2016 May 23. Insights Imaging. 2016. PMID: 27216793 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Evans HE, De Lahunta A. Miller’s anatomy of the dog. Saint Louis, MO: Elsevier Health Sciences; (2013). 658–671.
-
- Dewey CW, Da Costa RC. Practical guide to canine and feline neurology. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons; (2015). 29–52.
-
- Konig HE, Liebich HG. Veterinary anatomy of domestic animals. Stuttgart, Germany: Thieme; (2020). 520–526.
-
- Elameen RAAE. Measurement of normal brainstem diameter in Sudanese population using MRI. Diss: Sudan University of Science and Technology; (2016).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

