Ecotoxicological significance of bio-corona formation on micro/nanoplastics in aquatic organisms
- PMID: 37520083
- PMCID: PMC10375451
- DOI: 10.1039/d3ra04054b
Ecotoxicological significance of bio-corona formation on micro/nanoplastics in aquatic organisms
Abstract
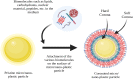
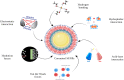
The unsustainable manufacturing, utilization and inadequate handling of plastics have led to a surge in global plastic pollution. In recent times, there has been increasing concern about the plausible hazards associated with exposure to micro/nanoplastics (M/NPs). As aquatic systems are considered to be the likely sink for M/NPs, it is crucial to comprehend their environmental behavior. The bioavailability, toxicity and fate of M/NPs in the environment are predominantly dictated by their surface characteristics. In the aquatic environment, M/NPs are prone to be internalized by aquatic organisms. This may facilitate their interaction with a diverse array of biomolecules within the organism, resulting in the formation of a biocorona (BC). The development of BC causes modifications in the physicochemical attributes of the M/NPs including changes to their size, stability, surface charge and other properties. This review details the concept of BC formation and its underlying mechanism. It provides insight on the analytical techniques employed for characterizing BC formation and addresses the associated challenges. Further, the eco-toxicological implications of M/NPs and the role of BC in modifying their potential toxicity on aquatic organisms is specified. The impact of BC formation on the fate and transport of M/NPs is discussed. A concise outlook on the future perspectives is also presented.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Khoaele K. K. Gbadeyan O. J. Chunilall V. Sithole B. Sustainability. 2023;15:5233.
-
- Lakkimsetty N. R., Al Rahbi B., Karunya S., Kavitha G. and Gundu S., in AIP Conference Proceedings, AIP Publishing LLC, 2023, vol. 2690, p. 20051
-
- Ivleva N. P. Wiesheu A. C. Niessner R. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017;56:1720–1739. - PubMed
-
- Kruse K., Knickmeier K., Brennecke D., Unger B. and Siebert U., in Marine Mammals: A Deep Dive into the World of Science, Springer International Publishing Cham, 2023, pp. 49–62
-
- Lebreton L. Andrady A. Palgrave Commun. 2019;5:1–11.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials