Rapid synthesis of functional poly(ester amide)s through thiol-ene chemistry
- PMID: 37520100
- PMCID: PMC10375450
- DOI: 10.1039/d3ra03478j
Rapid synthesis of functional poly(ester amide)s through thiol-ene chemistry
Abstract
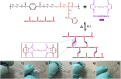
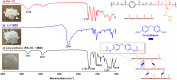
Poly(ester amide)s (PEAs) bearing various side chains were synthesized by post-polymerization modification of PA-1, a vinylidene containing PEA. The thiols 1-dodecanethiol (1A-SH), 2-phenylethanethiol (1B-SH), 2-mercaptoethanol (1C-SH), thioglycolic acid (1D-SH), furfuryl mercaptan (1E-SH) and sodium-2-mercaptoethanesulfonate (1F-SH) were reacted with PA-1 to form PEAs PA-1A through PA-1F respectively. PEAs containing non-polar thiol side chains (PA-1A, PA-1B, PA-1E), showed little change in solubility compared to PA-1, while PEAs with more polar side chains improved solubility in more polar solvents. PA-1F, functionalized with sodium-2-mercaptoethanesulfonate, became water-soluble. The introduction of pendant functional groups impacted the thermal behaviors of PEAs in a wide range. The PEAs were thermally stable up to 368 °C, with glass transition temperatures (Tg) measured between 117 to 152 °C. Moreover, to demonstrate the versatility of the PEAs, thermal reprocessable networks and polyurethanes were successfully fabricated by reacting with a bismaleimide (1,6-bis(maleimido)hexane, 1,6-BMH) and a diisocyanate (4,4'-diphenylmethane diisocyanate, 4,4'-MDI), respectively. This study paves the way for the facile synthesis of functional poly(ester amide)s with great potential in many fields.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Synthesis and characterization of biodegradable poly(ester amide)s with pendant amine functional groups and in vitro cellular response.Biomacromolecules. 2009 Nov 9;10(11):3037-47. doi: 10.1021/bm9006437. Biomacromolecules. 2009. PMID: 19810736
-
Enzymatically and reductively degradable α-amino acid-based poly(ester amide)s: synthesis, cell compatibility, and intracellular anticancer drug delivery.Biomacromolecules. 2015 Feb 9;16(2):597-605. doi: 10.1021/bm501652d. Epub 2015 Jan 17. Biomacromolecules. 2015. PMID: 25555025
-
Synthesis and characterization of ionic charged water soluble arginine-based poly(ester amide).J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2011 Mar;22(3):469-79. doi: 10.1007/s10856-011-4243-5. Epub 2011 Feb 3. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2011. PMID: 21287243
-
Recent Advances of Poly(ester amide)s-Based Biomaterials.Biomacromolecules. 2022 May 9;23(5):1892-1919. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.2c00150. Epub 2022 Apr 18. Biomacromolecules. 2022. PMID: 35435654 Review.
-
Recent advances in the development of poly(ester amide)s-based carriers for drug delivery.Saudi Pharm J. 2024 Jul;32(7):102123. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2024.102123. Epub 2024 Jun 1. Saudi Pharm J. 2024. PMID: 38911279 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Winnacker M. Rieger B. Poly(ester amide)s: recent insights into synthesis, stability and biomedical applications. Polym. Chem. 2016;7(46):7039–7046.
-
- Fonseca A. C. Gil M. H. Simões P. N. Biodegradable poly(ester amide)s – A remarkable opportunity for the biomedical area: Review on the synthesis, characterization and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014;39(7):1291–1311.
-
- Sun H. Meng F. Dias A. A. Hendriks M. Feijen J. Zhong Z. α-Amino Acid Containing Degradable Polymers as Functional Biomaterials: Rational Design, Synthetic Pathway, and Biomedical Applications. Biomacromolecules. 2011;12(6):1937–1955. - PubMed
-
- Wu J. Wu D. Mutschler M. A. Chu C.-C. Cationic Hybrid Hydrogels from Amino-Acid-Based Poly(Ester Amide): Fabrication, Characterization, and Biological Properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012;22(18):3815–3823.
-
- Han S. Wu J. Recent Advances of Poly(Ester Amide)s-Based Biomaterials. Biomacromolecules. 2022;23(5):1892–1919. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

