Arteriolosclerosis CSVD: a common cause of dementia and stroke and its association with cognitive function and total MRI burden
- PMID: 37520130
- PMCID: PMC10375409
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1163349
Arteriolosclerosis CSVD: a common cause of dementia and stroke and its association with cognitive function and total MRI burden
Abstract
Objective: Arteriolosclerosis cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD) is a common type of CSVD. This study aimed to explore the factors associated with cognitive function and total MRI burden related to the disease.
Methods: The demographic characteristics, clinical manifestations, cognitive function score, Barthel Index (BI), blood test index, and follow-up results of arteriolosclerosis CSVD patients treated for the first time in our hospital from January 2014 to August 2022 were collected. White matter hyperintensity (WMH) Fazekas score, total MRI burden, and cerebral atrophy grade were evaluated according to brain MRI findings. Factors associated with CSVD cognitive function were analyzed by binary logistic regression. The correlative factors related to the total MRI burden of CSVD were analyzed by ordered multiple logistic regression.
Results: A total of 146 patients were included in this study, of which 132 cases (90.4%) had hypertension. There were 108 patients (74.0%) with cognitive dysfunction, 97 patients (66.4%) with balance and gait disorders, and 83 patients (56.8%) with moderate-to-severe dependence in daily life (BI ≤ 60 points). Of 146 patients, 79 (54.1%) completed clinical and imaging follow-ups for a median of 3 years. The number of patients with cognitive impairment and BI ≤ 60 points after follow-up significantly increased compared with the first admission (P < 0.001). There were also significant differences in total MRI burden (P = 0.001), WMH Fazekas score, and cerebral atrophy grade (P < 0.001). Mean age (P = 0.012), median deep WMH Fazekas score (P = 0.028), and median deep (P < 0.001) and superficial (P =0.002) cerebral atrophy grade of patients with cognitive impairment at first admission were all higher than those with non-cognitive impairment. Multivariate analysis showed that deep cerebral atrophy was independently and significantly associated with cognitive impairment of CSVD (P = 0.024), and hypertension was significantly and independently associated with total MRI burden (P = 0.001).
Conclusion: The disease course of arteriolosclerosis CSVD may be related to cognitive function and total MRI burden. Deep cerebral atrophy was an independent risk factor for cognitive dysfunction in arteriolosclerosis CSVD, and hypertension was an independent risk factor for total MRI burden.
Keywords: cerebral atrophy; cerebral microbleed; cerebral small vessel disease; cognitive impairment; lacunar infarcts; white matter hyperintensities.
Copyright © 2023 Hua, Ma, Liu, Ji, Zhang, Xu, Chen and Mao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
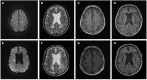
Similar articles
-
Heterogeneity of White Matter Hyperintensity and Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Acute Lacunar Stroke.Brain Sci. 2022 Dec 6;12(12):1674. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12121674. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 36552134 Free PMC article.
-
Total Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Burden on MRI Correlates With Medial Temporal Lobe Atrophy and Cognitive Performance in Patients of a Memory Clinic.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Sep 8;13:698035. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.698035. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34566621 Free PMC article.
-
Association between frailty index based on routine laboratory tests and risk of cerebral small vessel disease in elderly patients: a hospital-based observational study.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2022 Nov;34(11):2683-2692. doi: 10.1007/s40520-022-02207-8. Epub 2022 Aug 4. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2022. PMID: 35925517
-
Cerebral Small Vessel Disease.Cell Transplant. 2018 Dec;27(12):1711-1722. doi: 10.1177/0963689718795148. Epub 2018 Sep 25. Cell Transplant. 2018. PMID: 30251566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypertension-Induced Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Leading to Cognitive Impairment.Chin Med J (Engl). 2018 Mar 5;131(5):615-619. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.226069. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018. PMID: 29483399 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Carotid artery stenosis is related to cerebral small vessel disease magnetic resonance imaging burden.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 13;10(16):e36052. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36052. eCollection 2024 Aug 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39224254 Free PMC article.
-
Contributions of cerebral white matter hyperintensities, age, and pedal perception to postural sway in people with HIV.AIDS. 2024 Jul 1;38(8):1153-1162. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000003894. Epub 2024 Mar 27. AIDS. 2024. PMID: 38537080 Free PMC article.
-
ARTS is associated with vascular risk factors, MCI, dementia, and stroke.Alzheimers Dement. 2025 Jul;21(7):e70430. doi: 10.1002/alz.70430. Alzheimers Dement. 2025. PMID: 40588724 Free PMC article.
-
Brain iron deposition and cognitive decline in patients with cerebral small vessel disease : a quantitative susceptibility mapping study.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025 Jan 9;17(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01638-x. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 39789638 Free PMC article.
-
Contributions of Cerebral White Matter Hyperintensities to Postural Instability in Aging With and Without Alcohol Use Disorder.Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2024 Oct;9(10):998-1009. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2024.03.005. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2024. PMID: 38569932
References
-
- Diaz K. M., Veerabhadrappa P., Kashem M. A., Thakkar S. R., Feairheller D. L., Sturgeon K. M., et al. . (2013). Visit-to-visit and 24-h blood pressure variability: association with endothelial and smooth muscle function in African Americans. J. Hum. Hypertens. 27, 671–677. 10.1038/jhh.2013.33 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

