The effect of JQ1 systemic administration on oxidative stress and apoptotic markers in renal ischemic reperfusion injury in a rat model
- PMID: 37520478
- PMCID: PMC10375347
- DOI: 10.25122/jml-2022-0287
The effect of JQ1 systemic administration on oxidative stress and apoptotic markers in renal ischemic reperfusion injury in a rat model
Abstract
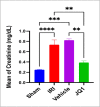
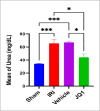
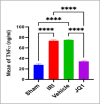
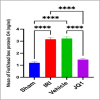
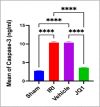
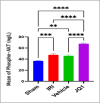
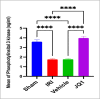
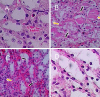
This study aimed to investigate the effects of JQ1 in a renal ischemia-reperfusion (IR) rat model. Twenty-four adult male Wistar Albino rats were randomly divided into four equal groups. The sham group underwent laparotomy without ischemia-reperfusion induction. The control group experienced bilateral renal ischemia for 30 minutes, followed by a 2-hour reperfusion period. The vehicle group (IR group + DMSO) and JQ1 group (same as in control IR + 25 mg/kg JQ1). Kidney and blood samples were collected 2 hours after reperfusion. Blood samples were used to analyze serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen levels. Renal tissue was assessed for TNF-alpha, caspase-3, FOXO4, PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, and histological analysis. The control group exhibited significantly higher serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, caspase-3, TNF-alpha, and FOXO4 levels in renal tissue compared to the sham group. Additionally, the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway was significantly decreased in the control group. Histopathological examination revealed severe kidney damage in the control group compared to the sham group. In rats treated with JQ1, serum creatinine, BUN, caspase-3, TNF-alpha, and FOXO4 levels in renal tissue significantly improved. The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway was substantially increased (p-value 0.01) compared to the Vehicle and Control groups. The tubular severity score was also significantly reduced in the JQ1-treated groups compared to the Control and Vehicle groups. In conclusion, JQ1 significantly ameliorated renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by suppressing apoptosis and inflammatory pathways.
Keywords: FOXO4; JQ1; PI3K/AKT; TNF-alpha; caspase-3; ischemia reperfusion injury.
©2023 JOURNAL of MEDICINE and LIFE.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
