The Radius of Curvature of the Inferior Distal Clavicle Is Similar to That of the Glenoid in Both the Axial and Coronal Planes and Similar to the Inferior Coracoid
- PMID: 37520505
- PMCID: PMC10382879
- DOI: 10.1016/j.asmr.2023.100777
The Radius of Curvature of the Inferior Distal Clavicle Is Similar to That of the Glenoid in Both the Axial and Coronal Planes and Similar to the Inferior Coracoid
Abstract
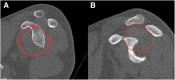
Purpose: The purposes of this study were to use computed tomography (CT) scans to compare the radius of curvature (ROC) of the inferior concave surface of the distal clavicle to the glenoid, determine graft dimensions, and compare the ROC of the congruent-arc distal clavicle autograft (DCA) to the congruent-arc Latarjet graft.
Methods: Patients who underwent bony glenoid reconstruction via a Laterjet procedure between January 2018 and January 2023 at a single institution were retrospectively identified. CT scans were used to measure the ROC of the glenoid on the axial and coronal sequences, measure the ROC of the distal clavicle on the sagittal oblique sequences, and determine the dimensions of the distal clavicle and coracoid graft.
Results: A total of 42 patients were included (Latarjet, n = 22; control, n = 20). The mean ROC of the inferior surface of the distal clavicle was not significantly different from the ROC of the glenoid in the coronal (P = .15) or axial planes (P = .65). The ROC of the coracoid when measured in the sagittal plane was not significantly different from the ROC of the distal clavicle (P = .25). The length, depth, and surface area of the coracoid in the congruent arc orientation were significantly larger than the distal clavicle (P < .005). Patients in the control group tended to have both a larger inferior clavicle ROC and a larger coracoid ROC compared to the Latarjet group (32.8 mm vs 29.6 mm, P < .0001; 31.8 mm vs 30.9 mm, P = .02).
Conclusions: The ROC of the inferior distal clavicle is similar to that of the glenoid in both the axial and coronal planes and similar to the inferior coracoid.
Clinical relevance: CT analysis reveals that the congruent-arc DCA technique provides a robust graft with dimensions that are suitable for reconstruction of the anterior glenoid.
© 2023 The Authors.
Figures




References
-
- Armitage M.S., Elkinson I., Giles J.W., Athwal G.S. An anatomic, computed tomographic assessment of the coracoid process with special reference to the congruent-arc Latarjet procedure. Arthroscopy. 2011;27(11):1485–1489. - PubMed
-
- de Beer J.F., Roberts C. Glenoid bone defects—open Latarjet with congruent arc modification. Orthop Clin North Am. 2010;41(3):407–415. - PubMed
-
- Dehaan A., Munch J., Durkan M., Yoo J., Crawford D. Reconstruction of a bony Bankart lesion: Best fit based on radius of curvature. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(5):1140–1145. - PubMed
-
- Ghodadra N., Gupta A., Romeo A.A., et al. Normalization of glenohumeral articular contact pressures after Latarjet or iliac crest bone-grafting. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(6):1478–1489. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

