Intravesical BCG in bladder cancer induces innate immune responses against SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 37520557
- PMCID: PMC10374029
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1202157
Intravesical BCG in bladder cancer induces innate immune responses against SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
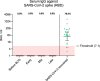
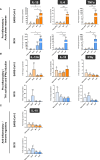
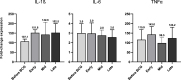
BCG is the most efficient adjuvant therapy for high-risk, non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC). Both innate and adaptive immune responses have been implicated in BCG-mediated effects. BCG vaccination can boost innate immune responses via trained immunity (TI), resulting in an increased resistance to respiratory viral infections. Here we evaluated for the first time whether intravesical application of BCG triggers increased immunity against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with high-risk NMIBC. Serum and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from heparinized whole blood samples of 11 unvaccinated SARS-CoV-2-naïve high-risk NMIBC patients were collected at baseline and during BCG treatment in a pre-COVID-19 era. To examine B-cell or T cell-dependent adaptive immunity against SARS-CoV-2, sera were tested for the presence of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies. Using a SARS-CoV-2 peptide pool, virus-specific T cells were quantified via IFNγ ELISpot assays. To analyze innate immune responses, mRNA and protein expression levels of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines were measured after a 24-hour stimulation of PBMCs with either BCG or SARS-CoV-2 wildtype. ATAC- sequencing was performed to identify a potential epigenetic reprogramming in immune cells. We neither identified SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies nor SARS-CoV-2- reactive T cells, indicating that intravesical BCG did not induce adaptive immunity against SARS-CoV-2. However, a significant increase in mRNA as well as protein expression of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNFα, which are key cytokines of trained immunity, could be observed after at least four intravesical BCG instillations. Genomic regions in the proximity of TI genes (TLR2, IGF1R, AKT1, MTOR, MAPK14, HSP90AA1) were more accessible during BCG compared to baseline. Although intravesical BCG did not induce adaptive immune responses, repetitive intravesical instillations of BCG induced circulating innate immune cells that produce TI cytokines also in response to SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: BCG; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; bladder cancer; trained immunity; viral infections.
Copyright © 2023 Pichler, Diem, Hackl, Koutník, Mertens, D`Andrea, Pradere, Soria, Mari, Laukhtina, Krajewski, Teoh, Del Guidice, Moschini, Thurnher and Posch.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Intravesical BCG in patients with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer induces trained immunity and decreases respiratory infections.J Immunother Cancer. 2023 Jan;11(1):e005518. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-005518. J Immunother Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36693678 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Aerosol Delivered BCG Vaccination on Immunological and Disease Parameters Following SARS-CoV-2 Challenge in Rhesus Macaques.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 9;12:801799. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.801799. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35222355 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of different Bacillus Calmette-Guerin substrains on growth inhibition of T24 bladder cancer cells and cytokines secretion by BCG activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells of PBMCs.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2014 Nov-Dec;23(6):877-84. doi: 10.17219/acem/37330. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2014. PMID: 25618112
-
Can BCG vaccine protect against COVID-19 via trained immunity and tolerogenesis?Bioessays. 2021 Mar;43(3):e2000200. doi: 10.1002/bies.202000200. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Bioessays. 2021. PMID: 33169410 Review.
-
Trained immunity as a molecular mechanism for BCG immunotherapy in bladder cancer.Nat Rev Urol. 2020 Sep;17(9):513-525. doi: 10.1038/s41585-020-0346-4. Epub 2020 Jul 16. Nat Rev Urol. 2020. PMID: 32678343 Review.
Cited by
-
No Association Between BCG Instillations and COVID-19 Incidence in a Dutch Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Cohort.Bladder Cancer. 2023 Dec 13;9(4):355-363. doi: 10.3233/BLC-230088. eCollection 2023. Bladder Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38994242 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Training the synergy between Bacillus Calmette-Guérin and immune checkpoint-blocking antibodies in bladder cancer.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2025 Apr;45(4):438-441. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12647. Epub 2025 Jan 10. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2025. PMID: 39797503 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ribal MJ, Cornford P, Briganti A, Knoll T, Gravas S, Babjuk M, et al. . European Association of urology guidelines office rapid reaction group: an organisation-wide collaborative effort to adapt the European association of urology guidelines recommendations to the coronavirus disease 2019 era. Eur Urol (2020) 78(1):21–8. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.04.056 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

