Cytokine response and damages in the lungs of aging Syrian hamsters on a high-fat diet infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus
- PMID: 37520568
- PMCID: PMC10375707
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1223086
Cytokine response and damages in the lungs of aging Syrian hamsters on a high-fat diet infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus
Abstract
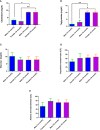
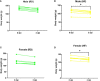
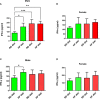
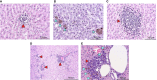
Hypertriglyceridemia, obesity, and aging are among the key risk factors for severe COVID-19 with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). One of the main prognostic biomarkers of ARDS is the level of cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α in the blood. In our study, we modeled hyperglyceridemia and hypercholesterolemia on 18-month-old Syrian hamsters (Mesocricetus auratus). By 18 months, the animals showed such markers of aging as weight stabilization with a tendency to reduce it, polycystic liver disease, decreased motor activity, and foci of alopecia. The high-fat diet caused an increase in triglycerides and cholesterol, as well as fatty changes in the liver. On the third day after infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus, animals showed a decrease in weight in the groups with a high-fat diet. In the lungs of males on both diets, there was an increase in the concentration of IFN-α, as well as IL-6 in both males and females, regardless of the type of diet. At the same time, the levels of TNF-α and IFN-γ did not change in infected animals. Morphological studies of the lungs of hamsters with SARS-CoV-2 showed the presence of a pathological process characteristic of ARDS. These included bronchointerstitial pneumonia and diffuse alveolar damages. These observations suggest that in aging hamsters, the immune response to pro-inflammatory cytokines may be delayed to a later period. Hypertriglyceridemia, age, and gender affect the severity of COVID-19. These results will help to understand the pathogenesis of COVID-19 associated with age, gender, and disorders of fat metabolism in humans.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; Syrian hamster; cytokine response; high-fat diet.
Copyright © 2023 Fomin, Tabynov, Islamov, Turebekov, Yessimseit and Yerubaev.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

