Fractional order epidemiological model of SARS-CoV-2 dynamism involving Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 37520617
- PMCID: PMC9525244
- DOI: 10.1016/j.health.2022.100114
Fractional order epidemiological model of SARS-CoV-2 dynamism involving Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
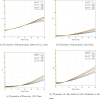
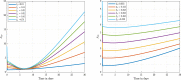
In this paper, we study a Caputo-Fabrizio fractional order epidemiological model for the transmission dynamism of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 pandemic and its relationship with Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's disease is incorporated into the model by evaluating its relevance to the quarantine strategy. We use functional techniques to demonstrate the proposed model stability under the Ulam-Hyres condition. The Adams-Bashforth method is used to determine the numerical solution for our proposed model. According to our numerical results, we notice that an increase in the quarantine parameter has minimal effect on the Alzheimer's disease compartment.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Caputo–Fabrizio fractional derivatives; Numerical scheme; SARS-CoV-2 pandemic; Ulam–Hyres stability.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization AIDS Report . 2021. Fact sheets about HIV AIDS. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hiv-aids.
-
- Sigdel A., Bista A., Bhattarai N., et al. 2020. Depression, anxiety and depression-anxiety comorbidity amid covid-19 pandemic: an online survey conducted during lockdown in Nepal. MedRxiv:2020.04.30.20086926. - DOI
-
- Meda N., Pardini S., Slongo I., et al. 2020. COVID-19 and depressive symptoms in students before and during lockdown. MedRxiv [Preprint] - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
