Artificial Intelligence and COVID-19: A Systematic umbrella review and roads ahead
- PMID: 37520766
- PMCID: PMC8831917
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jksuci.2021.07.010
Artificial Intelligence and COVID-19: A Systematic umbrella review and roads ahead
Abstract
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has played a substantial role in the response to the challenges posed by the current pandemic. The growing interest in using AI to handle Covid-19 issues has accelerated the pace of AI research and resulted in an exponential increase in articles and review studies within a very short period of time. Hence, it is becoming challenging to explore the large corpus of academic publications dedicated to the global health crisis. Even with the presence of systematic review studies, given their number and diversity, identifying trends and research avenues beyond the pandemic should be an arduous task. We conclude therefore that after the one-year mark of the declaration of Covid-19 as a pandemic, the accumulated scientific contribution lacks two fundamental aspects: Knowledge synthesis and Future projections. In contribution to fill this void, this paper is a (i) synthesis study and (ii) foresight exercise. The synthesis study aims to provide the scholars a consolidation of findings and a knowledge synthesis through a systematic review of the reviews (umbrella review) studying AI applications against Covid-19. Following the PRISMA guidelines, we systematically searched PubMed, Scopus, and other preprint sources from 1st December 2019 to 1st June 2021 for eligible reviews. The literature search and screening process resulted in 45 included reviews. Our findings reveal patterns, relationships, and trends in the AI research community response to the pandemic. We found that in the space of few months, the research objectives of the literature have developed rapidly from identifying potential AI applications to evaluating current uses of intelligent systems. Only few reviews have adopted the meta-analysis as a study design. Moreover, a clear dominance of the medical theme and the DNN methods has been observed in the reported AI applications. Based on its constructive systematic umbrella review, this work conducts a foresight exercise that tries to envision the post-Covid-19 research landscape of the AI field. We see seven key themes of research that may be an outcome of the present crisis and which advocate a more sustainable and responsible form of intelligent systems. We set accordingly a post-pandemic research agenda articulated around these seven drivers. The results of this study can be useful for the AI research community to obtain a holistic view of the current literature and to help prioritize research needs as we are heading toward the new normal.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence; Covid-19; Deep learning; Foresight analysis; Machine learning; Robotic; Umbrella review.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


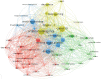



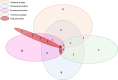
References
-
- Aalst V.D., Bichler M., Heinzl A. Robotic process automation. Bus Inf. Syst. Eng. 2018;60(2018):269–272. doi: 10.1007/s12599-018-0542-4. - DOI
-
- Adadi A. A survey on data-efficient algorithms in big data era. J. Big Data. 2021;8(1) doi: 10.1186/s40537-021-00419-9. - DOI
-
- Adadi A., Berrada M. Peeking inside the black-box: A survey on explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) IEEE Access. 2018;6:52138–52160.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
