Effects of regular aerobic exercise on vascular function in overweight or obese older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37520931
- PMCID: PMC10372915
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jesf.2023.06.002
Effects of regular aerobic exercise on vascular function in overweight or obese older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Overweight and obese older adults have a high risk for developing cardiovascular disease. Aerobic exercise is a valuable strategy to improve vascular health, but the effects of aerobic exercise on vascular endothelial function in obese and overweight older adults remain controversial. The purpose of this meta-analysis was to investigate the effects of aerobic exercise on vascular function in obese and overweight older adults with or without comorbidity.
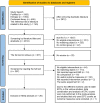
Methods: A systematic literature search for related studies published in English was conducted between January 1989 and October 30, 2022, in the PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases. A random effects model was chosen for meta-analysis, which calculated the effect sizes of control and intervention groups after exercise intervention using standardized mean differences (SMDs) corrected for Hedges' g bias and 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs).
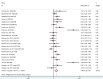
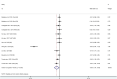
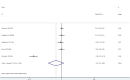
Results: Twenty-six studies containing 1418 participants were included in the study. After excluding three studies contributing to higher heterogeneity by sensitivity analysis, there are small effects of regular aerobic exercise on vascular function of obese and overweight older adults, including flow-mediated dilation (FMD) [SMD = 0.21, 95% CI (0.02, 0.41), z = 2.16, df = 19, I2 = 52.2%, P = 0.031] and pulse wave velocity (PWV) [SMD = -0.24, 95% CI (-0.46, -0.02), z = 2.17, df = 10, I2 = 8.6%, P = 0.030], and no significant effect was observed on augmentation index (Aix). Subgroup analysis showed small effects of regular aerobic exercise on FMD [SMD = 0.37, 95% CI (0.13, 0.61), z = 3.05, df = 9, I2 = 52.6%, P = 0.002] in the overweight not obese subgroup (25 = BMI <30 kg/m2), but no significant effect on the obese subgroup (BMI ≥30 kg/m2). Regular aerobic exercise for more than 24 weeks improved FMD by small effect sizes [SMD = 0.48, 95% CI (0.04, 0.93), z = 2.12, df = 5, I2 = 56.4%, P = 0.034] and for more than three times per week improved FMD by moderate effect sizes [SMD = 0.55, 95% CI (0.12, 0.98), z = 2.50, df = 3, I2 = 31.1%, P = 0.012] in obese and overweight older adults with or without CVD.
Conclusion: In obese and overweight older adults with or without comorbidity, regular aerobic exercise for more than 24 weeks improved FMD by small effect sizes and exercise for more than three times per week improved FMD by moderate effect sizes and regular aerobic exercise reduced PWV by small effect sizes and had no influence on Aix. Taken together, it was recommended that obese and overweight older adults should adhere to regular aerobic exercise, training at least 3 times per week for better results.
Keywords: Aerobic exercise; Meta-analysis; Obesity; Older adults; Overweight; Vascular function.
© 2023 The Society of Chinese Scholars on Exercise Physiology and Fitness. Published by Elsevier (Singapore) Pte Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of aerobic exercise on executive function among overweight and obese children: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Psychol. 2024 Oct 28;15:1485610. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1485610. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39529725 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of exercise training on arterial stiffness in obese and overweight children: a meta-analysis.Eur J Pediatr. 2022 Jul;181(7):2633-2642. doi: 10.1007/s00431-022-04489-6. Epub 2022 Apr 30. Eur J Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35499629 Review.
-
High-intensity interval training improves the vascular endothelial function comparing moderate-intensity interval training in overweight or obese adults: A meta-analysis.Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2023 Feb;53:100-106. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2022.11.023. Epub 2022 Dec 7. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2023. PMID: 36657899
-
Short- and long-term effects of concurrent aerobic and resistance training on circulating irisin levels in overweight or obese individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.PeerJ. 2024 Sep 19;12:e17958. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17958. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39308824 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of aerobic, resistance and combined training on endothelial function and arterial stiffness in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 2;19(12):e0308600. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308600. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39621701 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Relationship between cardiorespiratory fitness and arterial health in young-, and middle-age women: A mediation effect of body composition.J Exerc Sci Fit. 2025 Oct;23(4):341-348. doi: 10.1016/j.jesf.2025.07.004. Epub 2025 Jul 16. J Exerc Sci Fit. 2025. PMID: 40703406 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Comparative effectiveness of statins and exercise in high-risk individuals: systematic review and network meta-analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jul 11;12:1617799. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1617799. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40718380 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of high-intensity interval exercise on arterial stiffness in individuals at risk for cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Apr 17;11:1376861. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1376861. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38694567 Free PMC article.
-
Association of circulating Notch1 and VEGF with flow-mediated dilation and aerobic fitness in healthy adults.Transl Exerc Biomed. 2025 May 28;2(2):74-82. doi: 10.1515/teb-2025-0006. eCollection 2025 Jul. Transl Exerc Biomed. 2025. PMID: 40641678 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Paneni F., Diaz Cañestro C., Libby P., Lüscher T.F., Camici G.G. The aging cardiovascular system: understanding it at the cellular and clinical levels. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;69:1952–1967. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous