Rheumatoid arthritis occurring after coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection: Case based review
- PMID: 37521095
- PMCID: PMC8894859
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejr.2022.03.001
Rheumatoid arthritis occurring after coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection: Case based review
Abstract
Introduction: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a multifactorial disease. Genetic predisposition and environmental triggers including infections are the major players of autoimmunity. We present a case of rheumatoid arthritis occurring after the coronavirus disease 2019(COVID-19) infection.
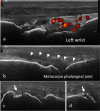
Case presentation: A 72-year-old woman with a medical history of hypertension and atrial fibrillation presented for a 2-month history of bilateral symmetric polyarthritis starting 2 weeks after asymptomatic COVID-19 infection. Physical examination showed swelling and tenderness of the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints, wrists, and knees. She had increased inflammatory biomarkers (C-reactive protein:108 mg/L, erythrocyte sedimentation rate: 95 mm, alpha-2 and gamma-globulins, interleukin 6: 16.5 pg/mL). Immunological tests revealed positive rheumatoid factor (128 UI/mL), anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies (200UI/mL), anti-nuclear antibodies (1:320), and anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG (12.24U/mL). She had the genotype: HLA-DRB1*04:11, HLA-DQB1*03:01, and HLA-DQB1* 03:02. Hands and feet radiographs did not show any erosion. Ultrasonography showed active synovitis and erosion of the 5th right metatarsal head. The diagnosis of RA was made. The patient received intravenous pulses of methylprednisolone (250 mg/day for 3 consecutive days) then oral corticosteroids (15 mg daily) and methotrexate (10 mg/week) were associated, leading to clinical and biological improvement.
Conclusion: Despite its rarity, physicians should be aware of the possibility of the occurrence of RA after COVID-19 infection. This finding highlights the autoimmune property of this emerging virus and raises further questions about the pathogenesis of immunological alterations.
Keywords: COVID-19; Immune dysregulation; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2021 Egyptian Society for Joint Diseases and Arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Hammam N., Tharwat S., Shereef R.R.E., Elsaman A.M., Khalil N.M., Fathi H.M., et al. Egyptian College of Rheumatology (ECR) COVID-19 Study Group. Rheumatology university faculty opinion on coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) vaccines: the vaXurvey study from Egypt. Rheumatol Int. 2021;41(9):1607–1616. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous