Deep recurrent Gaussian Nesterovs recommendation using multi-agent in social networks
- PMID: 37521128
- PMCID: PMC8994100
- DOI: 10.1007/s12530-022-09435-3
Deep recurrent Gaussian Nesterovs recommendation using multi-agent in social networks
Abstract
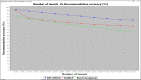
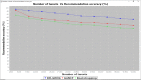
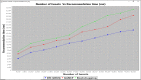
Due to increasing volume of big data the high volume of information in Social Network put a stop to users from acquiring serviceable information intelligently so many recommendation systems have emerged. Multi-agent Deep Learning gains rapid attraction, and the latest accomplishments address problems with real-world complexity. With big data precise recommendation has yet to be answered. In proposed work Deep Recurrent Gaussian Nesterov's Optimal Gradient (DR-GNOG) that combines deep learning with a multi-agent scenario for optimal and precise recommendation. The DR-GNOG is split into three layers, an input layer, two hidden layers and an output layer. The tweets obtained from the users are provided to the input layer by the Tweet Accumulator Agent. Then, in the first hidden layer, Tweet Classifier Agent performs optimized and relevant tweet classification by means of Gaussian Nesterov's Optimal Gradient model. In the second layer, a Deep Recurrent Predictive Recommendation model is designed to concentrate on the vanishing gradient issue arising due to updated tweets obtained from same user at different time instance. Finally, with the aid of hyperbolic activation function in the output layer, building block of the predictive recommendation is obtained. In the experimental study the proposed method is found better than existing GANCF and Bootstrapping method 13-21% in case of recommendation accuracy, 22-32% better in recommendation time and 15-22% better in recall rate.
Keywords: Big data; Deep recurrent; Gaussian Nesterov’s; Gradient; Predictive; Recommendation; Social network.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2022.
Figures






References
-
- Aivazoglou M, Roussos AO, Margaris D, Vassilakis C, Ioannidis S, Polakis J, Spiliotopoulos D (2020) A fine‑grained social network recommender system, Social network analysis and mining. Springer, New York [Bootstrapping]
-
- Angelov PP, Filev DP (2004) Flexible models with evolving structure. Int J Intell Syst 19(4):327–340
-
- Angelov PP, Gu X (2009) Empirical approach to machine learning, vol 800. Springer Nature, New York (ISBN: 978-3-030-02383-6)
-
- Angelov P, Soares E (2020) Towards explainable deep neural networks (xDNN). Neural Netw 130:185–194 - PubMed
-
- Azaouzi M, Romdhane LB (2018) An efficient two-phase model for computing influential nodes in social networks Using Social Actions. J Comput Sci Technol, Springer
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
