Proximity-Based Modalities for Biology and Medicine
- PMID: 37521793
- PMCID: PMC10375889
- DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.3c00395
Proximity-Based Modalities for Biology and Medicine
Abstract
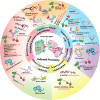
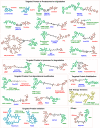
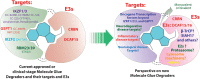
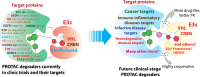
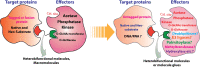
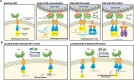
Molecular proximity orchestrates biological function, and blocking existing proximities is an established therapeutic strategy. By contrast, strengthening or creating neoproximity with chemistry enables modulation of biological processes with high selectivity and has the potential to substantially expand the target space. A plethora of proximity-based modalities to target proteins via diverse approaches have recently emerged, opening opportunities for biopharmaceutical innovation. This Outlook outlines the diverse mechanisms and molecules based on induced proximity, including protein degraders, blockers, and stabilizers, inducers of protein post-translational modifications, and agents for cell therapy, and discusses opportunities and challenges that the field must address to mature and unlock translation in biology and medicine.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): A.C. is a scientific founder, shareholder, and advisor of Amphista Therapeutics, a company that is developing targeted protein degradation therapeutic platforms. X.L. declares no conflicts.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

