Gynecology Resident Experience with Office Hysteroscopy Training
- PMID: 37522105
- PMCID: PMC10371772
- DOI: 10.4293/JSLS.2023.00009
Gynecology Resident Experience with Office Hysteroscopy Training
Abstract
Background: Hysteroscopy is the gold standard for evaluating intrauterine pathology. The majority of physicians currently perform hysteroscopy in the operating room. Lack of training has been cited as a barrier to performing office hysteroscopy; however, resident training in office hysteroscopy has not yet been evaluated.
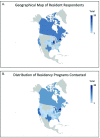
Methods: A prospective cross-sectional survey was performed. A validated 17 question survey tool was sent to 297 program directors of Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education accredited obstetrics and gynecology residency programs for distribution to their residents. The survey utilized a Likert scale to assess resident interest in learning office hysteroscopy, satisfaction in training, and perceived self-efficacy to perform office hysteroscopy independently upon graduation.
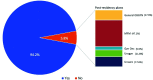
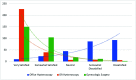
Results: Two hundred and ninety-three obstetrics and gynecology residents responded. Of the respondents, 26.3% reported receiving training in office hysteroscopy. There was no statistically significant difference in training among postgraduate years or program regions. A greater proportion of male residents received training when compared to female residents (42.9% vs. 24.2%, p = 0.019). Ninety-four percent of residents reported interest in learning office hysteroscopy. Satisfaction with hysteroscopy training in the operating room versus the office was 91.1% vs. 11.3% respectively. Of the fourth-year residents, 17.4% felt they could perform office hysteroscopy independently upon graduation and 14.5% reported feeling comfortable performing the procedure.
Conclusions: Residency training in office hysteroscopy is lacking and residents are unprepared to perform the procedure after graduation. Enhanced residency training in office hysteroscopy would likely improve resident comfort and ability to perform office hysteroscopy in practice.
Keywords: Curriculum; Education; Office Hysteroscopy; Residency.
© 2023 by SLS, Society of Laparoscopic & Robotic Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests: none.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resident and Program Director Confidence in Resident Surgical Preparedness in Obstetrics and Gynecologic Training Programs.Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Aug;136(2):369-376. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003990. Obstet Gynecol. 2020. PMID: 32649501
-
Obstetrics-gynecology resident long-acting reversible contraception training: the role of resident and program characteristics.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Apr;222(4S):S923.e1-S923.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2019.12.007. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020. PMID: 31866517
-
Fetal ultrasound training for obstetrics and gynecology residents.Obstet Gynecol. 2004 Feb;103(2):333-8. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000109522.51314.5c. Obstet Gynecol. 2004. PMID: 14754704
-
Resident and program director confidence in resident preparedness for operative vaginal deliveries in Obstetrics and Gynecology Training Programs in the United States.Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2022 Jan;4(1):100505. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2021.100505. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2022. PMID: 34656733
-
New technologies for safe practice and training during pregnancy: a gynecologist and forensic pathologist perspective narrative review.Front Surg. 2025 Jan 17;12:1513832. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2025.1513832. eCollection 2025. Front Surg. 2025. PMID: 39895899 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Use of Diode Laser in Hysteroscopy for the Management of Intrauterine Pathology: A Systematic Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Feb 2;14(3):327. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14030327. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38337843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Legal Lens on Hysteroscopy: A Retrospective Review of Medical Malpractice Claims of Hysteroscopic Procedures.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Jan 29;13(3):264. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13030264. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39942453 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of hysteroscopic training models: A review of the literature.Heliyon. 2024 May 22;10(11):e31698. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31698. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38947438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Satisfaction survey on graduates of standardised training for resident doctors in Guizhou Province, China.BMJ Open. 2024 Oct 4;14(10):e085789. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-085789. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39366715 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guntupalli SR, Doo DW, Guy M, et al. . Preparedness of obstetrics and gynecology residents for fellowship training. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126(3):559–568. - PubMed
-
- DeFrancesco MS. Patient safety in outpatient procedures. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2019;46(2):379–387. - PubMed
-
- Isaacson K. Office hysteroscopy: a valuable but under-utilized technique. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2002;14(4):381–385. - PubMed
-
- Loffer FD. The time has come to quit relying on a blind endometrial biopsy or dilation and curettage to rule out malignant endometrial changes. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26(7):1207–1208. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
