Partial Response to Antidepressant Treatment: The Role of Nutraceutical Compounds
- PMID: 37522109
- PMCID: PMC10375276
- DOI: 10.36131/cnfioritieditore20230303
Partial Response to Antidepressant Treatment: The Role of Nutraceutical Compounds
Abstract
Objective: Depression represents one of the most severe psychiatric disorders, characterized by low mood episodes, as well as loss of interest. Major Depressive Episodes (MDE) treatment relies primarily on monoaminergic prescriptions. However, although the presence of many antidepressant medications, their efficacy is still partial. A promising intervention to improve antidepressant treatment may be the use of adjunctive nutraceuticals. Aim of the present study was to assess the efficacy of a N-Acetyl-cysteine, S-Adenosyl-L-Methionine and Folic acid's combination for the treatment of depressive symptoms in a sample of MDE patients.
Method: Fifty outpatients with a MDE diagnosis in the context of different psychiatric disorders such as Major Depression, Bipolar Disorder, Anxiety disorders, and Personality disorders were recruited. The sample was divided into different groups based on the nutraceutical administration: a) concurrently with an AD (starter group); b) add-on to an already prescribed treatment; c) single treatment.
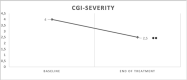
Results: A significant reduction of CGI-Severity and Improvement scores from baseline to the end of treatment was found. Moreover, the starter group showed a significantly greater CGI-Improvement score compared to the other groups. Ninety-four percent of patients did not show any side effects.
Conclusions: The present study showed promising results for the use of nutraceuticals in the add-on treatment of MDE. Those compounds may be considered a versatile, tolerable, and effective add-on treatment for the reduction of depressive symptoms impact and for improving the functioning of patients affected by MDE.
Keywords: adjunctive; major depressive episode; nutraceutical.
© 2023 Giovanni Fioriti Editore s.r.l.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: In the last three years, Prof. Dell’Osso has received lecture honoraria and grants from Angelini, Lundbeck, Janssen, Pfizer, Otzuka, Neuraxpharm, and Livanova. Prof. Benatti has received consulting fees from Janssen, Lundback, Angelini and honoraria from Angelini. The other authors have no conflicts to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Alvarez-Mon, M. A., Ortega, M. A., García-Montero, C., Fraile-Martinez, O., Monserrat, J., Lahera, G., Mora, F., Rodriguez-Quiroga, A., Fernandez-Rojo, S., Quintero, J., & Alvarez-Mon, M. (2021). Exploring the Role of Nutraceuticals in Major Depressive Disorder (MDD): Rationale, State of the Art and Future Prospects. Pharmaceuticals (Basel, Switzerland), 14(8), 821. 10.3390/ph14080821 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Arlington, VA. 10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596 - DOI
-
- Bedson, E., Bell, D., Carr, D., Carter, B., Hughes, D., Jorgensen, A., Lewis, H., Lloyd, K., McCaddon, A., Moat, S., Pink, J., Pirmohamed, M., Roberts, S., Russell, I., Sylvestre, Y., Tranter, R., Whitaker, R., Wilkinson, C., & Williams, N. (2014). Folate Augmentation of Treatment--Evaluation for Depression (FolATED): randomised trial and economic evaluation. Health technology assessment (Winchester, England), 18(48), vii–159. 10.3310/hta18480 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources