Facial and body contouring with 1444 nm Nd:YAG laser-assisted lipolysis: Clinical evidence
- PMID: 37522493
- PMCID: PMC10308064
- DOI: 10.1111/srt.13400
Facial and body contouring with 1444 nm Nd:YAG laser-assisted lipolysis: Clinical evidence
Abstract
Background: Body contouring is a significant area of dermatologic and plastic surgery. Surgical procedures, like surgical lipectomy, and less invasive procedures, such as various liposuction techniques, are the two main ways to reduce fat.
Aim: Our study showed that 1444 nm Nd:YAG laser-assisted lipolysis used with appropriate and specific parameters effectively destroys adipose tissue avoiding these risks and determining a safe clinical application.
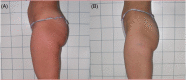
Method: A subcutaneous, 1444 nm Nd:YAG laser was used on 132 patients (range, 18-73 years; 109 women and 23 men with Fitzpatrick skin phototypes ranging between II and V) requiring body and face contouring. All patients were photographed for documentation. Digital clinical photography was taken under as near identical conditions as possible at baseline (pre-treatment), and 16 weeks post-treatment. The 5-point Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale (GAIS) was recorded immediately after treatment and at their final assessment session (4 months). Adverse events were monitored.
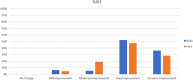
Results: On the basis of the investigator-evaluated GAIS scale, the total GAIS scores showed satisfactory results. Clinician assessment from the clinical photography showed good efficacy and visible aesthetic results for body and face areas. No serious or unexpected adverse side effects were recorded, and transient pain, oedema, erythema and slight induration resolved within the first week of treatment.
Conclusions: The 1444 nm Nd:YAG laser is a new tool for performing lipolysis, and this study reports its effectiveness and safety.
Keywords: 1444 nm Nd:YAG laser; GAIS scale; facial and body contouring; lipolysis.
© 2023 The Authors. Skin Research and Technology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
I.F. is employed at El.En. Group. The other authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Mann MW, Palm MD, Sengelmann RD. New advances in liposuction technology. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2008;27:72–82. - PubMed
-
- Kim KH, Geronemus RG. Laser lipolysis using a novel 1,064 nm Nd:YAG Laser. Dermatol Surg. 2006;32:241–248. - PubMed
-
- Goldman A. Submental Nd: Yag laser‐assisted liposuction Lasers. Surg Med. 2006;38:181–184. - PubMed
-
- Prado A, Andrades P, Danilla S, Leniz P, Castillo P, Gaete F. A prospective, randomized, double‐blind, controlled clinical trial comparing laser‐assisted lipoplasty with suction assisted lipoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;118:1032–1045. - PubMed
-
- Khoury JG, Saluja R, Keel D, Detwiler S, Goldman MP. Histologic evaluation of interstitial lipolysis comparing a 1064, 1320 and 2100 nm laser in an ex vivo model Lasers. Surg Med. 2008;40:402–406. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

