The clinical aspects of septo-optic dysplasia: A narrative review with illustrative case report
- PMID: 37524018
- PMCID: PMC10407208
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2023.108575
The clinical aspects of septo-optic dysplasia: A narrative review with illustrative case report
Abstract
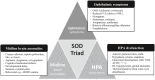
Introduction and importance: Septo-optic dysplasia (SOD) is a rare congenital disorder characterized by abnormal development of the optic nerve, pituitary gland, hypothalamus, and midline brain structures, with heterogeneous presentation among cases.
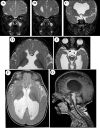
Case presentation: We report a seven-month-old male infant presented with persistent vomiting and delayed developmental milestones. He had dysmorphic facial features, bilateral esotropia, a head circumference of 50 cm, and scoliosis. His muscle tone was high (clasp-knife spasticity) and his deep tendon reflexes were brisk in the four limbs. Clinical evaluation and brain MRI confirmed the diagnosis of SOD, for which, he was subjected for multidisciplinary evaluation. Genetic testing revealed an autosomal dominant TUBB gene mutation. On follow-up, at the age of three years, he presented with recurrent focal motor and generalized seizures, which were controlled with levetiracetam.
Clinical discussion: The ophthalmic manifestations of SOD include optic nerve hypoplasia, which can lead to visual impairments such as nystagmus, strabismus, and reduced visual acuity. Midline brain anomalies involve structures like the corpus callosum and septum pellucidum, and can result in cognitive and neurological deficits. Hypothalamic-pituitary axis abnormalities can cause endocrine dysfunction and growth abnormalities. The clinical heterogeneity of SOD is attributed to variable phenotypic penetration and genetic mutations. Environmental risk factors may also contribute to the development of the syndrome.
Conclusion: SOD is a complex disorder with diverse clinical manifestations. Early diagnosis and multidisciplinary management are crucial for optimizing patient outcomes. Further research is needed to understand the underlying genetic and environmental factors involved in SOD and to develop targeted treatments.
Keywords: Case report; Clinical features; De Morsier syndrome; Midline brain anomalies; Optic nerve hypoplasia; Septo-optic dysplasia.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sataite I., Cudlip S., Jayamohan J., Ganau M. Septo-optic dysplasia. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2021;181:51–64. - PubMed
-
- Tuuli M.G., Odibo A.O. Elsevier; 2018. Septooptic Dysplasia; pp. 172–174.
-
- Back S.A., Plawner L.L. Elsevier; 2011. Congenital Malformations of the Central Nervous System; pp. 844–868.
-
- Agha R.A., Franchi T., Sohrab C., Mathew G., Kirwan A., Thomas A., et al. The SCARE 2020 guideline: updating consensus Surgical Case Report (SCARE) guidelines. Int. J. Surg. 2020;84(1):226–230. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

