Interleukin 17 signaling supports clinical benefit of dual CTLA-4 and PD-1 checkpoint inhibition in melanoma
- PMID: 37525015
- PMCID: PMC10518254
- DOI: 10.1038/s43018-023-00610-2
Interleukin 17 signaling supports clinical benefit of dual CTLA-4 and PD-1 checkpoint inhibition in melanoma
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Interleukin 17 signaling supports clinical benefit of dual CTLA-4 and PD-1 checkpoint inhibition in melanoma.Nat Cancer. 2023 Sep;4(9):1395. doi: 10.1038/s43018-023-00632-w. Nat Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37580519 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
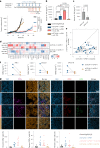
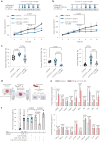
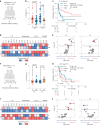
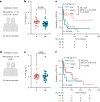
Recent studies suggest that BRAFV600-mutated melanomas in particular respond to dual anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and anti-cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) immune checkpoint inhibition (ICI). Here we identified an over-representation of interleukin (IL)-17-type 17 helper T (TH17) gene expression signatures (GES) in BRAFV600-mutated tumors. Moreover, high baseline IL-17 GES consistently predicted clinical responses in dual-ICI-treated patient cohorts but not in mono anti-CTLA-4 or anti-PD-1 ICI cohorts. High IL-17 GES corresponded to tumor infiltration with T cells and neutrophils. Accordingly, high neutrophil infiltration correlated with clinical response specifically to dual ICI, and tumor-associated neutrophils also showed strong IL-17-TH17 pathway activity and T cell activation capacity. Both the blockade of IL-17A and the depletion of neutrophils impaired dual-ICI response and decreased T cell activation. Finally, high IL-17A levels in the blood of patients with melanoma indicated a higher global TH17 cytokine profile preceding clinical response to dual ICI but not to anti-PD-1 monotherapy, suggesting a future role as a biomarker for patient stratification.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
D.S. served as a consultant and/or has received honoraria from Array, Roche, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Nektar, NeraCare, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, Philogen, Pfizer, Sandoz, Sun Pharma and Sanofi; research funding to their institution from Novartis, Amgen, Roche, MSD and Array; and travel support from Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pierre Fabre, Sun Pharma, Sanofi and Novartis, outside the submitted work. E.L. served as a consultant and/or has received honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi, Sun Pharma and Takeda and travel support from Bristol Myers Squibb, Pierre Fabre, Sun Pharma and Novartis, outside the submitted work. A.R. reports grants from Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb and Adtec; personal fees from Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb and Merck Sharp & Dohme; and nonfinancial support from Amgen, Roche, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb and Teva, outside the submitted work. W.P.F. reports fees from Calyx (consultant), RadioMedix (image review), Bayer (speaker bureau) and Parexel (image review), outside the submitted work. J.M.P. served as a consultant and/or has received honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis and Sanofi and has received travel support from Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis and Therakos, outside the submitted work. L.J.A. received honoraria from Novartis, Sun Pharma and Bristol Myers Squibb and travel support from Sun Pharma, Takeda and Sanofi, outside the submitted work. S.U. declares research support from Bristol Myers Squibb and Merck Serono; speaker and advisory board honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Merck Serono, Novartis and Roche and travel support from Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme and Pierre Fabre, outside the submitted work. W.S. reports grants from medi, grants and personal fees from Novartis and Almirall and personal fees from Amgen, AbbVie, Janssen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Lilly, UCB Novartis, Pfizer, LEO Pharma and Sanofi Genzyme, outside the submitted work. J.C.B. reports employment with Novartis and ownership of Novartis stock. D.G. reports employment with Novartis. J.U. is on the advisory board or has received honoraria and travel support from Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, GSK, Immunocore, Leo Pharma, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, Roche and Sanofi, outside the submitted work. L.Z. declares speaker and advisory board honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, research support from Novartis and travel support from Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi, Sun Pharma and Novartis, outside the submitted work. H.C.R. received consulting and lecture fees from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Roche, Bristol Myers Squibb, Vertex, SinABiomedics and Merck. H.C.R. received research funding from AstraZeneca and Gilead Pharmaceuticals. H.C.R. is a cofounder of CDL Therapeutics. D.S.T. reports grants from Bristol Myers Squibb and Asher Biotherapeutics and speaker honoraria from Boehringer Ingelheim and served as a consultant for Ysios Capital and iTEOS, outside the submitted work. T.A. reports personal fees from CeCaVa, institutional grants and personal fees from Novartis, institutional grants from NeraCare, personal fees and travel grants from BMS, personal fees from Pierre Fabre, institutional grants from Sanofi, institutional grants from SkylineDx and institutional grants from iFIT, outside the submitted work. All other authors declare no competing interest.
Figures



References
-
- Zimmer L, et al. Adjuvant nivolumab plus ipilimumab or nivolumab monotherapy versus placebo in patients with resected stage IV melanoma with no evidence of disease (IMMUNED): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2020;400:1117–1129. - PubMed
-
- Yao, Z. et al. Human IL-17: a novel cytokine derived from T cells. J. Immunol.155, 5483–5486 (1995). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

