Recent advances of exosomal circRNAs in cancer and their potential clinical applications
- PMID: 37525158
- PMCID: PMC10388565
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-023-04348-4
Recent advances of exosomal circRNAs in cancer and their potential clinical applications
Abstract
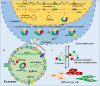
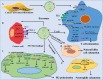
Circular RNA (circRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA that forms a covalently closed, uninterrupted loop. The expression of circRNA differs among cell types and tissues, and various circRNAs are aberrantly expressed in a variety of diseases, including cancer. Aberrantly expressed circRNAs contribute to disease progression by acting as microRNA sponges, functional protein sponges, or novel templates for protein translation. Recent studies have shown that circRNAs are enriched in exosomes. Exosomes are spherical bilayer vesicles released by cells into extracellular spaces that mediate intercellular communication by delivering cargoes. These cargoes include metabolites, proteins, lipids, and RNA molecules. Exosome-mediated cell-cell or cell-microenvironment communications influence the progression of carcinogenesis by regulating cell proliferation, angiogenesis, metastasis as well as immune escape. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge about exosomal circRNAs in cancers and discuss their specific functions in tumorigenesis. Additionally, we discuss the potential value of exosomal circRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers and the potential applications of exosomal circRNA-based cancer therapy.
Keywords: Cancer treatment; Disgnostic biomarker; Exosome; Tumorigenesis; circRNAs.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Collaborators GBDRF Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388(10053):1659–724. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31679-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schiffman JD, Fisher PG, Gibbs P. Early detection of cancer: past, present, and future. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2015;57–65. 10.14694/EdBook_AM.2015.35.57. - PubMed
-
- Alix-Panabieres C, Pantel K. Liquid biopsy: from discovery to clinical application. Cancer Discov. 2021;11(4):858–873. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-1311. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

