Partial Thyroid Hormone-Binding Globulin Deficiency: A Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 37525823
- PMCID: PMC10387242
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S413048
Partial Thyroid Hormone-Binding Globulin Deficiency: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
Background: Thyroxine binding globulin (TBG) deficiency is a rare thyroid disease, mostly caused by genetic mutations and acquired by X-linked recessive inheritance. The clinical features of children with TBG deficiency and their family members were summarised and the Serpina7 gene mutation was analysed, providing a reference for the differentiation of TBG deficiency.
Methods: Thyroid function was detected in TBG deficient patients, and genetic analysis was performed using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and direct DNA sequencing to detect the characteristics of TBG mutants. Using "thyroxine binding globulin, gene and mutation" as keywords, PubMed (biomedical literature database), Web of Science and other databases were searched for relevant studies to collect and summarise relevant information.
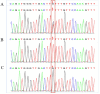
Results: The TBG (14.7 μg/mL), 70% triiodothyronine (T3) (<0.3 nmol/L), total T3 (Tr3) (<0.05 ng/mL) and thyroxine (T4) (14.72 nmol/L) values were lower than normal, while the thyrotropin (TSH) (2.33 uIU/mL), free T3 (FT3) (1.62 pmol/L), and free T4 (FT4) (11.39 pmol/L) values were normal. These values indicate a TBG partially deficient phenotype. Using PCR amplification and direct sequencing of the target gene, a missense mutation in exon 4 of the Serpina7 gene was found in the patient and the father, and the nucleic acid variant was C.909 (exon 4) g > T; the patient was heterozygous and the father was hemizygous. The literature search retrieved a total of 45 studies, most of which were related to mutations in the Serpina7 gene. The mutation locations included exons, introns, enhancers and promoters, with exons the predominant location. A total of 49 variants of the Serpina7 gene were identified.
Conclusion: Serpina7 C.909G (P.L303F) is a mutation acquired from the father by X-linked recessive inheritance. The main clinical features of TBG deficiency patients are low serum T4, T3 and TBG levels, normal TSH, FT3 and FT4 levels, and no clinical manifestations.
Keywords: deficiency; genes; mutation; thyroxine-binding globulin.
© 2023 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors had no personal, financial, commercial, or academic conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Dang PP, Xiao WW, Shan ZY, et al. Novel frameshift mutation causes early termination of the thyroxine-binding globulin protein and complete thyroxine-binding globulin deficiency in a Chinese family: a case report. World J Clin Cases. 2019;7(22):3887–3894. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i22.3887 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous