Inhibition of autotaxin alleviates pathological features of hepatic encephalopathy at the level of gut-liver-brain axis: an experimental and bioinformatic study
- PMID: 37528089
- PMCID: PMC10394058
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-023-06022-5
Inhibition of autotaxin alleviates pathological features of hepatic encephalopathy at the level of gut-liver-brain axis: an experimental and bioinformatic study
Abstract
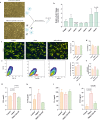
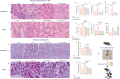
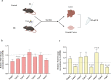
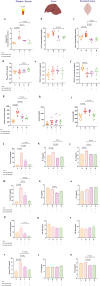
There is accumulating evidence that the circulatory levels of autotaxin (ATX) and lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) are increased in patients with severe liver disease. However, the potential role of the ATX-LPA axis in hepatic encephalopathy (HE) remains unclear. Our study aimed to investigate the role of the ATX-LPA signaling pathway in mice with thioacetamide (TAA) induced acute HE. To show the role of the ATX-LPA axis in the context of HE, we first measured the involvement of ATX-LPA in the pathogenesis of TAA-induced acute HE. Then, we compared the potential effects of ATX inhibitor (HA130) on astrocyte responses at in vitro and gut-liver-brain axis at in vivo levels. The inflammatory chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3 was significantly increased in the hyperammonemic condition and could be prevented by ATX inhibition in astrocytes at in vitro level. Further statistical tests revealed that plasma and tissue pro-inflammatory cytokines were inhibited by HA130 in mice. Furthermore, the stage of HE was significantly improved by HA130. The most surprising result was that HA130 alleviated immune infiltrating cells in the liver and intestine and decreased mucus-secreting cells in the intestine. Further analysis showed that the levels of liver enzymes in serum were significantly decreased in response to ATX inhibition. Surprisingly, our data indicated that HA130 could recover permeabilization of the blood-brain barrier, neuroinflammation, and recognition memory. Besides that, we found that the changes of Interleukin-1 (IL-1) and aquaporin-4 (AQP4) in HE might have a connection with the glymphatic system based on bioinformatics analyses. Taken together, our data showed that the ATX-LPA axis contributes to the pathogenesis of HE and that inhibition of ATX improves HE.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Sun X, Lv Y, Huang L, Gao H, Ren C, Li J, et al. Pro-inflammatory cytokines serve as communicating molecules between the liver and brain for hepatic encephalopathy pathogenesis and Lycium barbarum polysaccharides protection. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;248:112357. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112357. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Trovato FM, Zia R, Artru F, Mujib S, Jerome E, Cavazza A, et al. Lysophosphatidylcholines modulate immunoregulatory checkpoints in peripheral monocytes and are associated with mortality in people with acute liver failure. J Hepatol. 2022;78:558–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

