Thin film epitaxial [111] Co[Formula: see text]Pt[Formula: see text]: structure, magnetisation, and spin polarisation
- PMID: 37528131
- PMCID: PMC10394051
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-37825-3
Thin film epitaxial [111] Co[Formula: see text]Pt[Formula: see text]: structure, magnetisation, and spin polarisation
Abstract
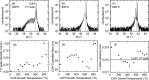
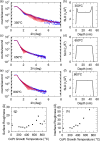
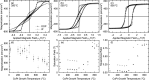
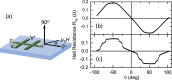
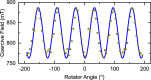
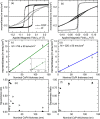
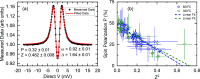
Ferromagnetic films with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy are of interest in spintronics and superconducting spintronics. Perpendicular magnetic anisotropy can be achieved in thin ferromagnetic multilayer structures, when the anisotropy is driven by carefully engineered interfaces. Devices with multiple interfaces are disadvantageous for our application in superconducting spintronics, where the current perpendicular to plane is affected by the interfaces. Robust intrinsic PMA can be achieved in certain Co[Formula: see text]Pt[Formula: see text] alloys and compounds at any thickness, without increasing the number of interfaces. Here, we grow equiatomic Co[Formula: see text]Pt[Formula: see text] and report a comprehensive study on the structural, magnetic, and spin-polarisation properties in the [Formula: see text] and [Formula: see text] ordered compounds. Primarily, interest in Co[Formula: see text]Pt[Formula: see text] has been in the [Formula: see text] crystal structure, where layers of Pt and Co are stacked alternately in the [100] direction. There has been less work on [Formula: see text] crystal structure, where the stacking is in the [111] direction. For the latter [Formula: see text] crystal structure, we find magnetic anisotropy perpendicular to the film plane. For the former [Formula: see text] crystal structure, the magnetic anisotropy is perpendicular to the [100] plane, which is neither in-plane or out-of-plane in our samples. We obtain a value for the ballistic spin polarisation of the [Formula: see text] and [Formula: see text] Co[Formula: see text]Pt[Formula: see text] to be [Formula: see text].
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pt and CoB trilayer Josephson [Formula: see text] junctions with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy.Sci Rep. 2021 May 27;11(1):11173. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90432-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34045523 Free PMC article.
-
Superconductivity assisted change of the perpendicular magnetic anisotropy in V/MgO/Fe junctions.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 24;11(1):19041. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-98079-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34561472 Free PMC article.
-
Critical switching current density of magnetic tunnel junction with shape perpendicular magnetic anisotropy through the combination of spin-transfer and spin-orbit torques.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 24;11(1):22842. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02185-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34819554 Free PMC article.
-
Perpendicular Magnetic Anisotropy in Heusler Alloy Films and Their Magnetoresistive Junctions.Materials (Basel). 2018 Jan 11;11(1):105. doi: 10.3390/ma11010105. Materials (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29324709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and superconducting properties of CaC6.Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2009 Jan 28;9(4):044102. doi: 10.1088/1468-6996/9/4/044102. eCollection 2008 Dec. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2009. PMID: 27878015 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Piramanayagam SN. Perpendicular recording media for hard disk drives. J. Appl. Phys. 2007;102:011301. doi: 10.1063/1.2750414. - DOI
-
- Linder J, Robinson JW. Superconducting spintronics. Nat. Phys. 2015;11:307–315. doi: 10.1038/nphys3242. - DOI
-
- Manchon A, et al. Current-induced spin-orbit torques in ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic systems. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2019;91:035004. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.91.035004. - DOI
-
- Bass J, Pratt WP. Spin-diffusion lengths in metals and alloys, and spin-flipping at metal/metal interfaces: An experimentalist’s critical review. J. Condens. Matter Phys. 2007;19:183201. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/19/18/183201. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

