Development of a prediction model for neonatal hypoglycemia risk factors: a retrospective study
- PMID: 37529595
- PMCID: PMC10389046
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1199628
Development of a prediction model for neonatal hypoglycemia risk factors: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: It's challenging for healthcare workers to detect neonatal hypoglycemia due to its rapid progression and lack of aura symptoms. This may lead to brain function impairment for the newborn, placing a significant care burden on the family and creating an economic burden for society. Tools for early diagnosis of neonatal hypoglycemia are lacking. This study aimed to identify newborns at high risk of developing neonatal hypoglycemia early by developing a risk prediction model.
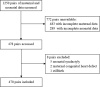
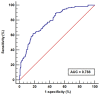
Methods: Using a retrospective design, pairs (470) of women and their newborns in a tertiary hospital from December 2021 to September 2022 were included in this study. Socio-demographic data and clinical data of mothers and newborns were collected. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression were used to screen optimized factors. A neonatal hypoglycemia risk nomogram was constructed using R software, and the calibration curve and receiver operator characteristic curve (ROC) was utilized to evaluate model performance.
Results: Factors integrated into the prediction risk nomogram were maternal age (odds ratio [OR] =1.10, 95% CI: 1.04, 1.17), fasting period (OR=1.07, 95% CI: 1.03, 1.12), ritodrine use (OR=2.00, 95% CI: 1.05, 3.88), gestational diabetes mellitus (OR=2.13, 95% CI: 1.30, 3.50), gestational week (OR=0.80, 95% CI: 0.66, 0.96), fetal distress (OR=1.76, 95% CI: 1.11, 2.79) and neonatal body mass index (OR=1.50, 95% CI: 1.24, 1.84). The area under the curve (AUC) was 0.79 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.75, 0.82), specificity was 0.82, and sensitivity was 0.62.
Conclusion: The prediction model of this study demonstrated good predictive performance. The development of the model identifies advancing maternal age, an extended fasting period before delivery, ritodrine use, gestational diabetes mellitus diagnosis, fetal distress diagnosis and an increase in neonatal body mass index increase the probability of developing neonatal hypoglycemia, while an extended gestational week reduces the probability of developing neonatal hypoglycemia.
Keywords: neonatal hypoglycemia; nomogram; predictive model; retrospective study; risk factors.
Copyright © 2023 Wu, Huang, Song, Redding, Huang and Ouyang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous