Genetic inhibitors of APOBEC3B-induced mutagenesis
- PMID: 37532520
- PMCID: PMC10620048
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.277430.122
Genetic inhibitors of APOBEC3B-induced mutagenesis
Abstract
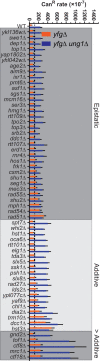
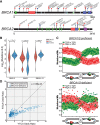
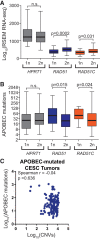
The cytidine deaminases APOBEC3A (A3A) and APOBEC3B (A3B) are prominent mutators of human cancer genomes. However, tumor-specific genetic modulators of APOBEC-induced mutagenesis are poorly defined. Here, we used a screen to identify 61 gene deletions that increase A3B-induced mutations in yeast. We also determined whether each deletion was epistatic with Ung1 loss, which indicated whether the encoded factors participate in the homologous recombination (HR)-dependent bypass of A3B/Ung1-dependent abasic sites or suppress A3B-catalyzed deamination by protecting against aberrant formation of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). We found that the mutation spectra of A3B-induced mutations revealed genotype-specific patterns of strand-specific ssDNA formation and nucleotide incorporation across APOBEC-induced lesions. Combining these three metrics, we were able to establish a multifactorial signature of APOBEC-induced mutations specific to (1) failure to remove H3K56 acetylation, (2) defective CTF18-RFC complex function, and (3) defective HR-mediated bypass of APOBEC-induced lesions. We extended these results by analyzing mutation data for human tumors and found BRCA1/2-deficient breast cancers display three- to fourfold more APOBEC-induced mutations. Mirroring our results in yeast, Rev1-mediated C-to-G substitutions are mainly responsible for increased APOBEC-signature mutations in BRCA1/2-deficient tumors, and these mutations associate with lagging strand synthesis during replication. These results identify important factors that influence DNA replication dynamics and likely the abundance of APOBEC-induced mutation during tumor progression. They also highlight a novel role for BRCA1/2 during HR-dependent lesion bypass of APOBEC-induced lesions during cancer cell replication.
© 2023 Mertz et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures




Update of
-
Genetic modifiers of APOBEC-induced mutagenesis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 6:2023.04.05.535598. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.05.535598. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Genome Res. 2023 Sep;33(9):1568-1581. doi: 10.1101/gr.277430.122. PMID: 37066362 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. 1995. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc B Methodol 57: 289–300. 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
