Regulation of the RNA polymerase II pre-initiation complex by its associated coactivators
- PMID: 37532915
- PMCID: PMC11088444
- DOI: 10.1038/s41576-023-00630-9
Regulation of the RNA polymerase II pre-initiation complex by its associated coactivators
Abstract
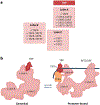
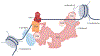
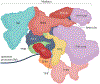
The RNA polymerase II (Pol II) pre-initiation complex (PIC) is a critical node in eukaryotic transcription regulation, and its formation is the major rate-limiting step in transcriptional activation. Diverse cellular signals borne by transcriptional activators converge on this large, multiprotein assembly and are transduced via intermediary factors termed coactivators. Cryogenic electron microscopy, multi-omics and single-molecule approaches have recently offered unprecedented insights into both the structure and cellular functions of the PIC and two key PIC-associated coactivators, Mediator and TFIID. Here, we review advances in our understanding of how Mediator and TFIID interact with activators and affect PIC formation and function. We also discuss how their functions are influenced by their chromatin environment and selected cofactors. We consider how, through its multifarious interactions and functionalities, a Mediator-containing and TFIID-containing PIC can yield an integrated signal processing system with the flexibility to determine the unique temporal and spatial expression pattern of a given gene.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Roeder RG Role of general and gene-specific cofactors in the regulation of eukaryotic transcription. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol 63, 201–218 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Thomas MC & Chiang CM The general transcription machinery and general cofactors. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol 41, 105–178 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Roeder RG The role of general initiation factors in transcription by RNA polymerase II. Trends Biochem. Sci 21, 327–335 (1996). - PubMed
-
- Buratowski S et al. Function of a yeast TATA element-binding protein in a mammalian transcription system. Nature 334, 37–42 (1988). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

