Ensifentrine as a Novel, Inhaled Treatment for Patients with COPD
- PMID: 37533771
- PMCID: PMC10392818
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S413436
Ensifentrine as a Novel, Inhaled Treatment for Patients with COPD
Abstract
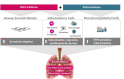
Ensifentrine is a novel, potent, and selective dual inhibitor of phosphodiesterase (PDE)3 and PDE4 designed for delivery by inhalation that combines effects on airway inflammation, bronchodilation and ciliary function in bronchial epithelia. In Phase 2 studies in subjects with COPD, ensifentrine demonstrated clinically meaningful bronchodilation and improvements in symptoms and health-related quality of life when administered alone or in combination with current standard of care therapies. Ensifentrine is currently in late-stage clinical development for the maintenance treatment of patients with COPD. This review summarizes non-clinical data as well as Phase 1 and Phase 2 efficacy and safety results of nebulized ensifentrine relevant to the maintenance treatment of patients with COPD.
Keywords: RPL554; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; clinical efficacy; drug development; nebulized therapy.
© 2023 Donohue et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Margot MacDonald-Berko, Tara Rheault, PhD, and Kathleen Rickard, MD are employees and shareholders of Verona Pharma. Thomas Bengtsson is a paid statistical consultant for Verona Pharma. James F Donohue, MD has consultant and advisory board relationships with Verona Pharma. Dr Kathleen Rickard has a patent Various pending to unknown. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD). Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease 2023 report; 2023. Available from: https://goldcopd.org/2023-gold-report-2/. Accessed July 4, 2023.
-
- de Boer J, Philpott AJ, Van amsterdam RG, Shahid M, Zaagsma J, Nicholson CD. Human bronchial cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isoenzymes: biochemical and pharmacological analysis using selective inhibitors. Br J Pharmacol. 1992;106:1028–1034. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14451.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

