Water scarcity in agriculture: An overview of causes, impacts and approaches for reducing the risks
- PMID: 37534016
- PMCID: PMC10392093
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18507
Water scarcity in agriculture: An overview of causes, impacts and approaches for reducing the risks
Abstract
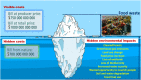
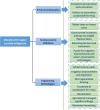
Freshwater is a vital resource for both ecosystem health and human survival, and it is the natural resource that is the most extracted at the global level. Excessive freshwater consumption can be responsible for a scarcity in the circulation rate, which occurs when the freshwater demand exceeds its availability. Hence, water consumption needs to be optimised in all human activities, given the increasing freshwater scarcity due to climate changes and to the annual net increase in the human population of 81,000,000. Freshwater plays many important roles in daily life for example, agriculture is responsible for nearly 70% of that withdrawal volume, and it is therefore, the most water-intensive sector. This puts emphasis upon the urgent need of transitioning towards more sustainable agricultural and food-production/consumption systems. Water Footprint (WF) is increasingly playing a guiding role in that context. Indeed, it makes it possible to quantify water consumption and related environmental consequences. With the objective of contributing to enhancement of research and of supporting practitioners and decision-makers in environmentally sustainable and resilient food production/consumption, the authors of this article addressed the relevant issues connected with: a) physical and economic water scarcity in agriculture, b) practices and tools to reduce water wastage, c) WF assessment methodologies. A number of environmental, economic, and engineering solutions were proposed to mitigate water scarcity. The improvement of irrigation technologies and practices was identified as an important major way to reduce water scarcity. Additionally, solar powered 'reverse-osmosis' is being used in many parts of the world to produce irrigation water from saline water, thereby reducing the need to extract freshwater from underground aquifers. This article confirmed the importance of research on water scarcity; moreover, it can stimulate development and application of solutions that make agricultural production/consumption more efficient and resilient.
Keywords: Environmental and social-economic effects; Human population growth; Mitigation solutions; Water footprint; Water scarcity.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Bayart J.-B., Bulle C., Deschênes L., Margni M., Pfister S., Vince F., Koehler A. A framework for assessing off-stream freshwater use in LCA. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2010;15(5):439–453.
-
- Layani G., Bakhshoodeh M., Zibaei M., Viaggi D. Sustainable water resources management under population growth and agricultural development in the Kheirabad river basin, Iran. Bio base Appl. Econ. 2021;10(4):305–323.
-
- Motoshita M., Itsubo N., Inaba A. Development of impact factors on damage to health by infectious diseases caused by domestic water scarcity. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2011;16(1):65–73.
-
- Pfister S., Koehler A., Hellweg S. Assessing the environmental impacts of freshwater consumption in LCA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009;43(11):4098–4104. - PubMed
-
- Meneses Y.E., Stratton J., Flores R.A. Water reconditioning and reuse in the food processing industry: current situation and challenges. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017;61:72–79.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

