The evolution of minimal residual disease: key insights based on a bibliometric visualization analysis from 2002 to 2022
- PMID: 37534257
- PMCID: PMC10391156
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1186198
The evolution of minimal residual disease: key insights based on a bibliometric visualization analysis from 2002 to 2022
Abstract
Background: The topic of minimal residual disease (MRD) has emerged as a crucial subject matter in the domain of oncology in recent years. The detection and monitoring of MRD have become essential for the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of various types of malignancy.
Aims: The purpose of this study is to explore the research trends, hotspots, and frontiers of MRD in the last two decades through bibliometric analysis.
Methods: We employed Web of Science databases to carry out a bibliometric visualization analysis of research on 8,913 academic papers about MRD research from 2002 to 2022. VOSviewer, CiteSpace, RStudio, and a bibliometric online analysis platform were mainly used to conduct co-occurrence analysis and cooperative relationship analysis of countries/regions, institutions, journals, and authors in the literature. Furthermore, co-occurrence, co-citation, and burst analyses of keyword and reference were also conducted to generate relevant knowledge maps.
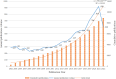
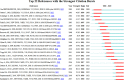
Results: In the past 20 years, the number of MRD research papers has presented an overall rising trend, going through three stages: a plateau, development, and an explosion. The output of articles in the United States was notably superior and plays a dominant role in this field, and the Netherlands had the highest average citation per article. The most productive and influential institution was the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. Blood published the most papers and was the most cited journal. A collection of leading academics has come to the fore in the research field, the most prolific of which is Kantarjian HM. It was found that the application of MRD in "acute myeloid leukemia", "acute lymphoblastic leukemia", "multiple myeloma", as well as the detection technology of MRD, are the research hotspots and frontiers in this domain. Furthermore, we analyzed the co-citation network of references and found that the top 10 co-cited references were all associated with MRD in hematological malignancies.
Conclusion: This bibliometric visualization analysis conducted a thorough exploration into the research hotspots and trends in MRD from 2002 to 2022. Our findings can aid researchers in recognizing possible collaborations, guiding future research directions, and fostering the growth of MRD detection and monitoring technologies.
Keywords: CiteSpace; VOSviewer; bibliometrics; hematological malignancies; minimal residual disease (MRD).
Copyright © 2023 Yu, Xie, Zhang, Lin and Niu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Research Trends in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: A Bibliometric and Network Visualization Study.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):254. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709254. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224012
-
Research hotspots and frontiers of machine learning in renal medicine: a bibliometric and visual analysis from 2013 to 2024.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Mar;57(3):907-928. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04259-3. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39472403 Review.
-
A bibliometric and visualization analysis of research trends and hotspots on targeted therapy for breast cancer from 2003 to 2022.Front Oncol. 2024 Jun 4;14:1366900. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1366900. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38894873 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric analysis of laryngeal cancer treatment literature (2003-2023).Heliyon. 2024 Dec 16;11(1):e40832. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40832. eCollection 2025 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39811326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Knowledge Structure and Emerging Trends of Telerehabilitation in Recent 20 Years: A Bibliometric Analysis via CiteSpace.Front Public Health. 2022 Jun 20;10:904855. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.904855. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35795695 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Implementation of a roadmap for the comprehensive diagnosis, follow-up, and research of childhood leukemias in vulnerable regions of Mexico: results from the PRONAII Strategy.Front Oncol. 2024 Apr 3;14:1304690. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1304690. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38634051 Free PMC article.
-
Application of circulating tumor DNA liquid biopsy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report and review of literature.World J Clin Cases. 2025 Jul 26;13(21):105066. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i21.105066. World J Clin Cases. 2025. PMID: 40726932 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Koschade SE, Stratmann JA, Finkelmeier F, Wagner S, Chromik J, Steffen B, et al. Relapse surveillance of acute myeloid leukemia patients in first remission after consolidation chemotherapy: diagnostic value of regular bone marrow aspirations. Ann Hematol (2022) 101(8):1703–10. doi: 10.1007/s00277-022-04862-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pulsipher MA, Han X, Maude SL, Laetsch TW, Qayed M, Rives S, et al. Next-generation sequencing of minimal residual disease for predicting relapse after tisagenlecleucel in children and young adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood Cancer Discov (2022) 3(1):66–81. doi: 10.1158/2643-3230.BCD-21-0095 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pui CH, Pei D, Coustan-Smith E, Jeha S, Cheng C, Bowman WP, et al. Clinical utility of sequential minimal residual disease measurements in the context of risk-based therapy in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a prospective study. Lancet Oncol (2015) 16(4):465–74. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)70082-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

