Neoadjuvant Camrelizumab Plus Platinum-Based Chemotherapy vs Chemotherapy Alone for Chinese Patients With Resectable Stage IIIA or IIIB (T3N2) Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The TD-FOREKNOW Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 37535377
- PMCID: PMC10401395
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2023.2751
Neoadjuvant Camrelizumab Plus Platinum-Based Chemotherapy vs Chemotherapy Alone for Chinese Patients With Resectable Stage IIIA or IIIB (T3N2) Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The TD-FOREKNOW Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: The benefit of neoadjuvant camrelizumab plus chemotherapy for resectable stage IIIA or IIIB non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains unknown.
Objective: To assess the efficacy and safety of neoadjuvant camrelizumab plus chemotherapy vs chemotherapy alone for patients with resectable stage IIIA or IIIB NSCLC.
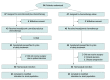
Design, setting, and participants: In this randomized phase 2 clinical trial conducted at 2 hospitals in China, patients aged 18 to 70 years with resectable stage IIIA or IIIB (T3N2) NSCLC were enrolled between April 7, 2020, and January 12, 2022.
Interventions: Patients were randomly assigned to receive 3 cycles of camrelizumab (200 mg) plus chemotherapy (nab-paclitaxel, 130 mg/m2, and platinum [cisplatin, 75 mg/m2; carboplatin, area under the curve, 5; or nedaplatin, 100 mg/m2]) or chemotherapy alone, followed by surgery after 4 to 6 weeks.
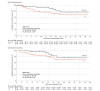
Main outcomes and measures: The primary end point was the pathologic complete response (pCR) rate. Secondary end points included the major pathologic response (MPR) rate, objective response rate (ORR), event-free survival (EFS), and safety. Disease-free survival (DFS, defined as the time from surgery to disease recurrence or death from any cause) was analyzed post hoc. Efficacy was assessed on a modified intention-to-treat basis.
Results: Ninety-four Chinese patients were randomized, and 88 (93.6%; median age, 61 years [IQR, 54-65 years]; 74 men [84.1%]) received allocated neoadjuvant treatment (43 received camrelizumab plus chemotherapy, and 45 received chemotherapy alone). Among these 88 patients, the pCR rate was 32.6% (14 of 43; 95% CI, 19.1%-48.5%) with camrelizumab plus chemotherapy vs 8.9% (4 of 45; 95% CI, 2.5%-21.2%) with chemotherapy alone (odds ratio, 4.95; 95% CI, 1.35-22.37; P = .008). The MPR rates were 65.1% (95% CI, 49.1%-79.0%) with camrelizumab plus chemotherapy and 15.6% (95% CI, 6.5%-29.5%) with chemotherapy alone. The radiographic ORRs were 72.1% (95% CI, 56.3%-84.7%) with camrelizumab plus chemotherapy and 53.3% (95% CI, 37.9%-68.3%) with chemotherapy alone. With a median follow-up of 14.1 months (IQR, 9.2-20.9 months), the median EFS and DFS were not reached in either group. The most common neoadjuvant treatment-related adverse events of grade 3 or higher were decreased white blood cell count (6 of 43 [14.0%] in the camrelizumab plus chemotherapy group vs 2 of 45 [4.4%] in the chemotherapy group) and decreased neutrophil count (3 of 43 [7.0%] in the camrelizumab plus chemotherapy group vs 5 of 45 [11.1%] in the chemotherapy group). No treatment-related deaths were reported.
Conclusions and relevance: This randomized clinical trial found that among patients with resectable stage IIIA or IIIB (T3N2) NSCLC, camrelizumab plus chemotherapy, compared with chemotherapy alone, significantly improved the pCR rate with manageable toxic effects.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04338620.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Liu J, Blake SJ, Yong MC, et al. Improved efficacy of neoadjuvant compared to adjuvant immunotherapy to eradicate metastatic disease. Cancer Discov. 2016;6(12):1382-1399. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0577 - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous